Every email marketing professional sending a campaign expects high open, reply, and conversion rates. Yet quite often, the spam rate takes over. This happens for two reasons – ESPs spam filter problems and the way the recipients interact with your emails. Unlike filters, based on algorithms and automatic analysis, the human factor is more unpredictable – if the message doesn’t correspond to the recipients’ needs or the content looks odd, they might mark it as spam.
Here we’ll cover everything you need to know about how to avoid spam filters and prevent your emails from being marked as spam.
Outline:
What is spam?
Spam (also known as junk email) is unsolicited emails sent in bulk to people who didn’t give their consent to receiving them with the purpose to promote, spread malware, or phish.
The key characteristics of spam emails are:
- Unsolicited
- Invisible headers
- Poor grammar and spelling
- Asking for suspicious actions or information
- Bulk sending (more than 10 recipients)
- Anonymous sender
- Spammy subject line
- Bright email body with lots of pictures, colors, and fonts
- Multiple links
- Irrelevant or suspicious attachments
All of these points can affect your email deliverability. However, there’s more to how emails end up in the spam folder than poor grammar and attachments. Let’s take a closer look.
How to prevent emails from going to Spam
Your emails can land in the Spam folder in two ways – by getting flagged by the email service providers’ (ESPs) spam filters or by having the recipient label your email as spam manually.
Email service providers analyze everything – how many of your emails you have sent before, how many emails you are trying to send right now, where you are sending them from, and how many of your emails get opened, which takes us to the human side of this problem.
How the recipients interact with your emails affects your sender reputation, which will then determine if you’ll be able to send emails again. Everything from email opens to spam complaints (obviously) affects it.
By avoiding suspicious behavior and fine-tuning your email copy you’ll maximize your deliverability and keep your reputation pristine.
How to avoid spam filter algorithms
As the first step of email analysis is conducted automatically by an algorithm, you need to be aware of the technical side and its influence on email deliverability.
1. Avoid using dynamic IPs
A dynamic IP is an address used by two or more people simultaneously, for example, when using the same ISP or local Wi-Fi connection (at work or in a cafe). If you use an IP previously used for purposes you can not control, you won’t be able to control this IP’s sender reputation. And as you know, low sender reputation means a higher chance of getting flagged as a spammer.
You need a dedicated IP address to be on the safe side. A dedicated IP is a unique IP address associated with a definite hosting account that only you have access to.
2. Check the IP reputation regularly
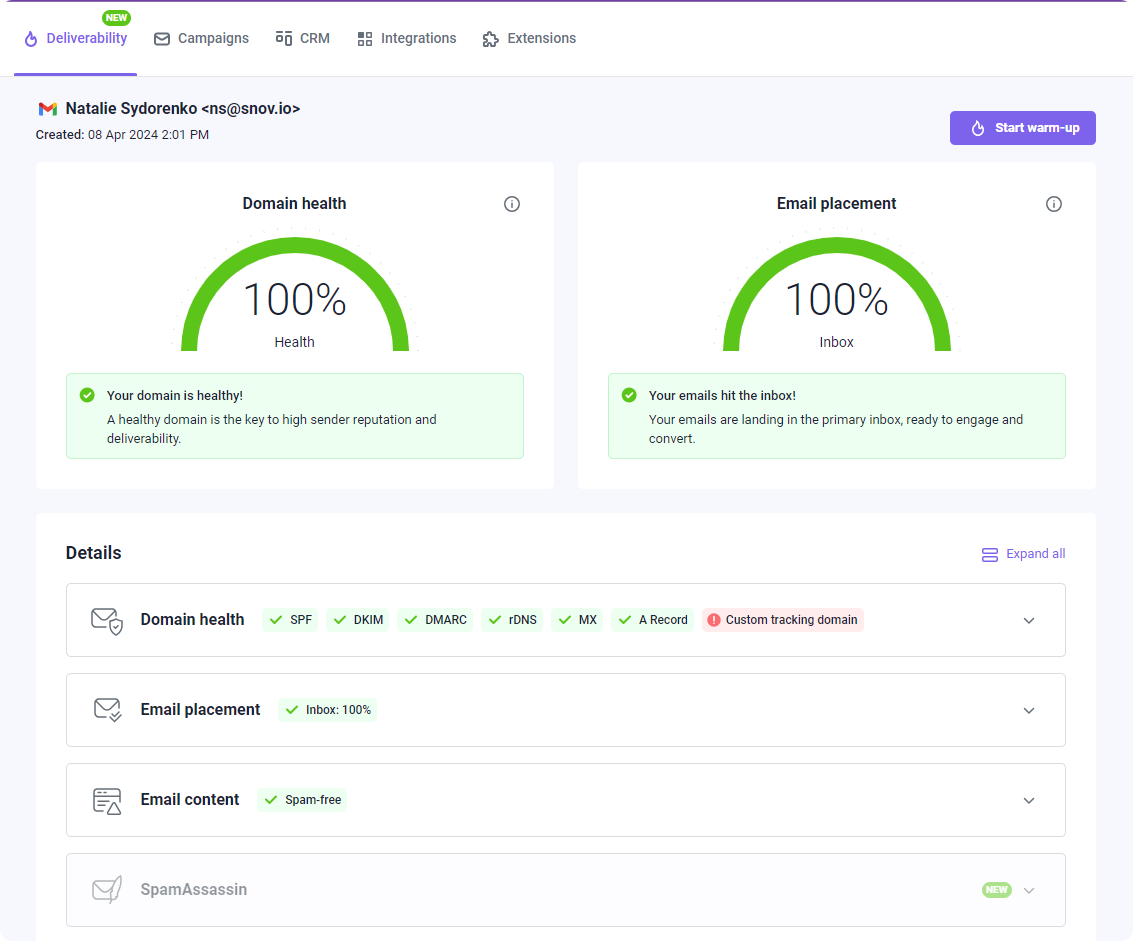
If you’re not sure about the reputation of your IP, you can always check it. There are numerous free apps that can help you do that. We recommend Snov.io, Talos Intelligence, or Sender Score for more detailed reports.
|
With Snov.io Deliverability Check, you can test your email domain’s technical setup and ensure your email content doesn’t trigger spam filters. The tool will provide you with Domain health score and Inbox score, so you’ll see what you should do to improve it.
|
3. Verify all email lists
First of all, we do not recommend purchasing email lists. That said, any email list you have, you have to verify, including those you have verified before. Regardless of the source, you cannot be 100% sure of the list’s quality, because emails get abandoned, mistyped, or blocked every day. As time passes, any email list will need a cleaning. So, why is verifying emails so important?
When you send emails to invalid email addresses, they bounce. The higher the bounce rate, the lower your IP reputation, and the lower your IP reputation, the closer you get to being blocked by the ESP.
So, you always need to be certain that the emails you send will reach real recipients. Plus, it’ll save you a big chunk of your budget. Always verify and test emails. You can choose an email tester based on your needs and business type.
4. Follow your email campaign open and spam complaint rates
Having low open and high spam complaint rates is the shortest way to being suspended by the ESPs. Follow how your campaign is performing, and edit accordingly to improve the results.
If it’s not helping, make sure to read our guide on how you can increase your email open rate. High unsubscribe and spam complaint rates are most likely caused by incorrectly chosen email frequency or the low quality of your email content.
If you need something to compare your rates to, here’s the all-industry average:
– the average open rate is 20.81% for B2C and 15.1% for B2B
– the average unsubscribe rate is 0.23%
– the spam complaint rate threshold (before you get suspended) is usually 0.5%.
5. Know the bounce rate
The bounce rate is the ratio of the emails that haven’t reached the recipients’ inboxes to the general number of sent emails. There’s a difference between hard and soft bounces, but the higher the bounce rate, the bigger the damage to your sender reputation. Of course, the ideal bounce rate is 0 but it’s not very realistic. Try to keep it under 2%.
6. Warm up new email accounts before sending large campaigns
If you deal with huge amounts of emails regularly and change your sender accounts from time to time, you need to first remember to warm them up. Start with one email a day (that is sure to be opened) and keep increasing this number day-to-day to improve your sender reputation.
To speed up the process, rely on an email warm-up tool such as Snov.io Email Warm-up. Thanks to AI-powered algorithms, it creates realistic emails and automatically sends them to the contacts database based on your chosen settings.
Your emails will get automatic replies, and if any of them lands in spam, Snov.io Email Warm-up will unspam them. This way, you’ll notice a considerable email deliverability improvement and open rate growth right after the first campaign.
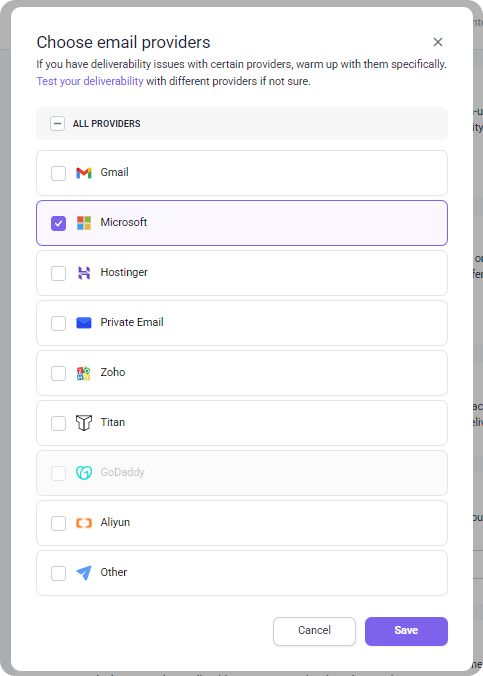
On top of that, now Snov.io lets you warm up emails for specific providers. Say, if you notice that your emails tend to land in spam on Microsoft accounts, you can fix the problem by warming up exactly this provider.
7. Create a separate email account for outbound marketing
When sending outbound email campaigns, you need to be 100% sure of your reputation. Unfortunately, it may be a daunting task when the whole company is using the same domain name and IP.
This is why many companies create a separate domain and account for outbound campaigns – to be able to control the sender reputation and have full confidence that they are the only ones responsible for it. It’s a good idea to keep all your email campaigns separated – outbound, marketing, newsletters, transactional emails, etc.
8. Set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are the three protection steps that can save senders from phishers, hackers, and data capture, and help avoid the recipients’ Spam folder.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is a special DNS record that contains all the IP addresses from which you can send emails from your domain name. The SPF check is the first step in email authentication. If the recipients’ server finds your sender IP in the SPF record, it will let the email pass through to the second check. Learn how to create an SPF record for your domain here.
Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) is the mechanism that works using two encryption keys, private and public. This is the second step in preventing spoofing. The private key encrypts an invisible header in every email. The public key is the TXT-record in the DNS record.
When the recipient’s server receives an email, it requests the public key and decrypts the header that proves that you are the sender. If you don’t set up the DKIM, many mail servers will simply decline your email. Read how to set up DKIM here.
Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) is a protocol that defines what to do if the sent email hasn’t passed the first two authentication steps (SPF and DKIM). This is the third and last step in email authentication. You can set one of three options: take no action on the email, mark the message as spam, or reject the message. Read how to set up DMARC here.
9. Avoid spam trigger words
Every sent email is analyzed in detail. Every word, too. If you overuse words that trigger spam filters, like free, 50% discount, buy now, etc., your emails may be sent to the Spam folder. You can read (and download) a list of 550+ spam trigger words we have compiled for you to keep your email copy clean.
10. Be careful with HTML
Badly coded HTML is a pretty distinctive feature of spammer emails, and the filters know it. Make sure your HTML template is perfect, or don’t use it at all.
11. Stick to the optimal text-to-picture ratio
Pictures are beloved by spammers because it’s a great way to hide spam trigger words from the filters. That’s why overusing pictures can catch the attention of spam filters. The best text-to-picture ratio is 80-to-20.
12. Send personalized emails
Spam is essentially bulk emails, sent with no regard to any personal approach. This means that spammers don’t bother with targeting and every email looks the same. And the spam filters are looking out for this. To avoid your emails looking like spam, you need to add a little personalization into each of your emails. This can be the person’s first name, last name, company, etc., there is no limit.
Not only will adding personalization help you avoid the filters, but it will also improve your open rate, click-through rate, and sometimes even conversions. Use custom email variables to add a human touch that will look real to both the ESPs’ filters and the recipients.
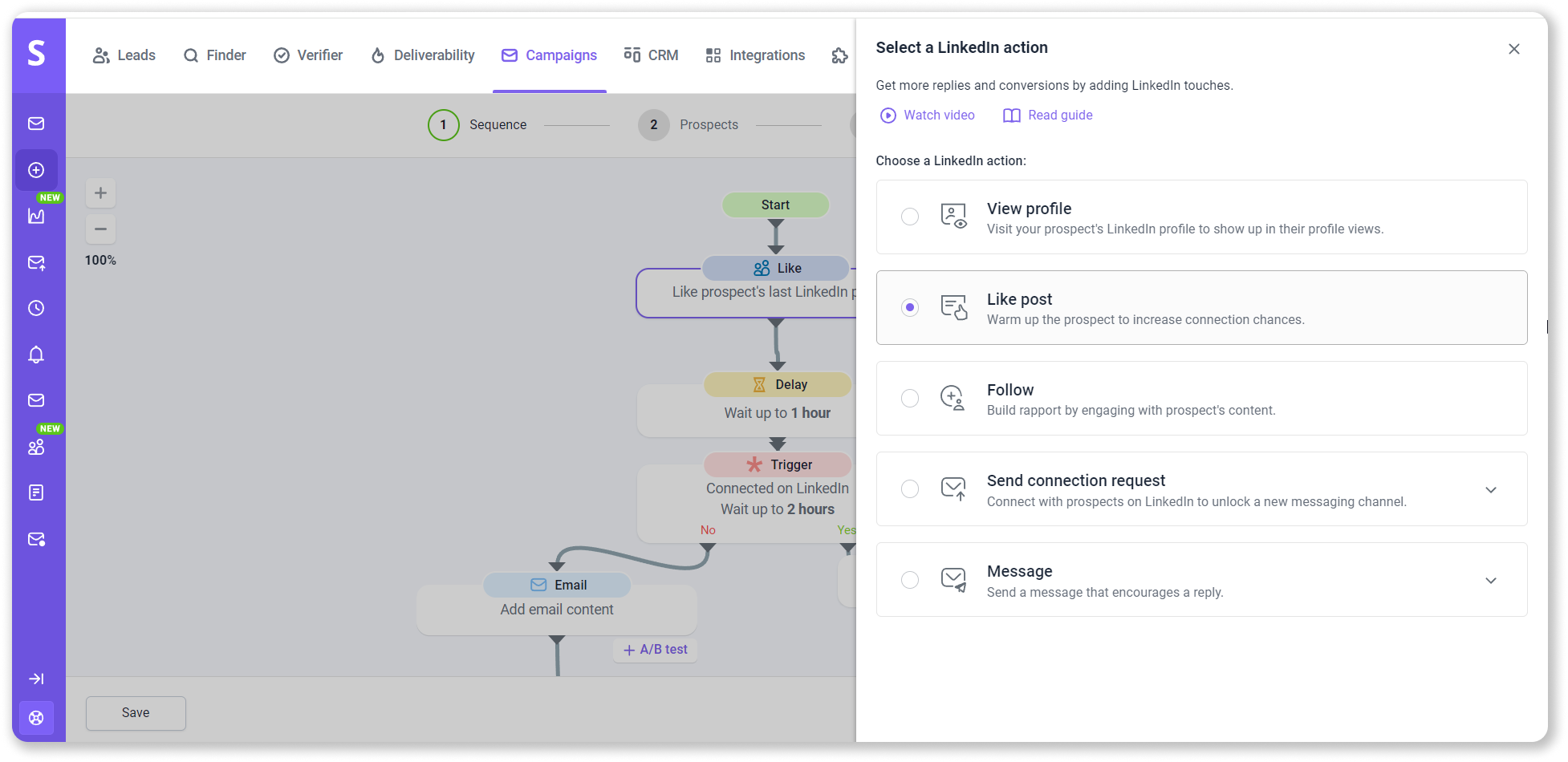
|
👀 Did you know? With Snov.io LinkedIn prospecting automation, you can send personalized connection requests and messages on LinkedIn! Just add these automated actions in Email Drip Campaigns and watch your client database grow.
|
13. Go easy on attachments
Email deliverability is majorly affected by the email size. Experiments show that the larger the email, the more often it is filtered as spam by ESPs. This way, the open and conversion rates decrease, and the spam rate grows.
The solution is easy: instead of sending the file as an attachment with the email, include links to Google Drive files (which, by the way, are automatically scanned for viruses and look trustworthy to both the ESPs and the recipients).
14. Comply with email laws and regulations
Under the CAN-SPAM Act, every sender should follow certain rules to be on the safe side. They are:
- Don’t send emails through open relays
- Include an unsubscribe link at the bottom of the email
- An email should contain the true header
- An email should contain at least one sentence and not be null
The CAN-SPAM Act is just one of the major regulations. Make sure your campaigns comply with the regulations of your (and your recipients’) country.
15. Track links right
Link tracking is crucial when it comes to analyzing your email campaign’s success. That said, it can hurt email deliverability if done wrong. The best way to include links in your email copy is by using anchor words instead of including the link as is. We explain this in more detail in our article about links tracking’s effect on deliverability.
How to reduce spam report rate
If the email content doesn’t suit the recipients’ expectations or they simply don’t want to receive emails from you, they can either unsubscribe or worse – if they suspect your email is spam they will send it to the Spam folder or report abuse to a blocklist center (SpamHaus, Talos Intelligence, etc). So, how do you reduce the spam report rate? By following a couple of rules (and common sense).
1. Receive people’s consent to emails
While cold email is a real and valid email marketing option, you’ll still get better results with inbound emails to people who have actively chosen to receive emails from you. When you receive people’s active consent to receive emails, you minimize the chances of them reporting your emails as spam. Set up a form on your website or inform buyers that you would like to send them emails to receive consent.
2. Learn how often people want to receive emails from you
If you receive emails from a certain sender too often, even if you’ve subscribed to them, you can still get annoyed into marking them as spam. Learn the email frequency best practices for B2B and B2C to avoid ruining your reputation and maximize your email marketing results.
3. Don’t use misleading subject lines and headers
Do not give false promises if you are not going to go through with them. Giving your emails misleading subject lines and headers will destroy the trust the recipients have in you when they open your emails and will increase your spam report rate. Learn how to write a great email subject line to improve your open rate, and never try to deceive your reader.
4. Use a clear and trustworthy sender name
The recipients are unlikely to trust you if they don’t know who you are. To avoid this you can:
- avoid obscure emails like 24446666668888888no@company.name
- don’t change your sender name too often
- make it recognizable by including your full name or the name of the company you work for (e.g. Maryna from Snov.io, Eileen at Zapier)
5. Avoid multiple colors, fonts, and capitalized text
Besides beings negatively perceived by spam filters, an overabundance of colors, fonts, and capitalized text can also awake distrust in the recipient. If the opened email contains hard-to-read text in multiple colors, with every sentence written in a different font, and the subject line or big chunks of text are in caps, it will scream SPAM to anyone who’s been online long enough to know what a spam email looks like.
However, if you’d still like to play with your fonts and colors a little without hurting your sender reputation, we’ve created guides on how to use fonts in an email and using colors in email marketing.
The gist is – don’t use more than two easy-to-read colors (one for the main text or background and one for the CTA), use one font, and once and for all forget about CAPS – no need to yell at your recipient. Ideally, use only your corporate colors and fonts to make your emails visually recognizable and trustworthy.
6. Let the recipient know you’re sending a promotional email
According to the CAN-SPAM Act, if an email is promotional or an advertisement, it should be disclosed in the email body. You can add this information at the end of the email. For example, This advertisement was sent by Company Name.
7. Double-check your grammar and spelling
Avoiding grammar and spelling mistakes as an email marketer is less advice and more common sense, but it’s especially relevant in the context of spam complaints. Poor grammar and spelling are a distinct feature of spammers. The exact reasons behind this are unclear – perhaps misspelling words helps avoid certain spam filters, or maybe phishers simply don’t pay much attention to the quality of their lies.
One thing is clear – mistakes don’t look good in the eyes of your recipients, and an overwhelmingly large number of mistakes can cause enough disappointment and anger to send your email to the spam folder.
8. Insert just one link with a clear CTA
If you want your CTAs to work, your link has to look legit. Therefore, make sure it describes clearly where it’s going to take the recipient – suspicious links are one of the primary reasons emails get labeled as spam. Besides, use just one link with the CTA – using multiple CTAs distracts the recipient from the main goal.
9. Ask for simple innocuous actions
What do you do if the sender asks you to send money? Or open an attachment you aren’t expecting? Or follow a sketchy link? I always mark such messages as spam. And who wouldn’t? Learn from others’ mistakes and do not ask people to perform questionable actions.
10. Allow recipients to unsubscribe
Everyone should have the right to unsubscribe if the content of the emails they receive doesn’t correspond with their needs, preferences, or wishes. Always give the recipient a way to opt-out, whether through a reply (best for outbound) or an unsubscribe link (inbound).
11. Do not send emails to generic corporate email addresses
Sending to generic email addresses like info@company.name, sales@company.name, etc. is unlikely to result in a high response rate and gives little room for personalization. None of this is good for your sender reputation. Which is why we recommend to send emails to personal corporate email addresses and personalize your email copy as much as possible.
Always be on the safe side
All the mentioned tips are crucial when sending an email campaign. However, sometimes things go wrong even in the best-planned campaigns, which is why you should always send a test email.
You can find lots of tools that check if the email you’re going to send will pass through all the spam filters. However, replicating the real conditions is the only sure way to find out if your email will reach the inbox. Send a spam test email to make sure you didn’t forget any of the points.
Happy sending!