TL;DR:
Bounce back emails occur when your message fails to reach a recipient and returns with an SMTP error code, indicating the reason for a failure. It can be a temporary issue (soft bounce) or a permanent problem (hard bounce).
Consider the most typical SMTP error codes for soft and hard bounces with their descriptions, possible solutions, and Snov.io tools that might help you fix and prevent bounce backs, improve deliverability, and send with confidence.
| Soft bounces | Hard bounces | |
|---|---|---|
| SMTP error codes | 421, 450, 451, 452 | 550, 551, 552, 554 |
| Description | Temporary issues, such as a full inbox, greylisting, or server unavailability. | Permanent issues connected with invalid emails, blacklisted IP addresses, or non-existent domains. |
| Possible solutions | Wait and retry after some time, clear the inbox, retry after the greylisting period, or connect in another way. | Remove invalid addresses, check domain health, and unblock the email address. |
| Snov.io tools to help | Email warm-up, Cold email tool, LinkedIn automation tool | Email verifier, Deliverability test, Mailbox rotation, Domain health checkup |
One of the best ways to avoid email bounce back is to find pre-verified email addresses and exclude any invalid contacts from your email lists.
The following post will provide more detailed recommendations on how to resolve the bounce issues.
Have you ever clicked the ‘Send’ button only to immediately receive a notification in your inbox that your email wasn’t delivered for some reason? I bet you have. This is commonly referred to as a ‘bounce back email.’
Luckily, now you’ll know why your messages bounced back, affecting your email deliverability rate. This post will help you fix the email bounce back problem, keeping your inbox placement under control.
Outline:
What is a bounce back email?
A bounce back email is a message from your service provider, indicating that your email didn’t reach the intended recipient due to certain issues. As a rule, this email flies to your inbox as an NDR (Non-Delivery Report), providing details about the delivery failure and its technical causes.
Where do bounces occur in the delivery chain?
Bounces typically occur at different stages in the SMTP handshake process.
SMTP, which stands for The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, is a standard method used for sending emails from one server to another. So, the SMTP handshake refers to the steps involved in the communication between your (a sender’s) server and a recipient’s server.
In simple words, when you send an email, your server attempts a “handshake” with a recipient’s server. If the recipient’s server rejects your message for some reason, it responds with an SMTP error code, which indicates the stage and reason of failure. Then you receive this data as a bounce back email generated by your server.
Think of the SMTP handshake as the path your email takes. If all checks pass, your message is delivered. If something goes wrong (invalid address, mailbox full, domain blocked, etc.), the handshake fails, and you receive an email bounce back.
Why bounces are a problem
Ask anyone involved in email outreach (especially marketers or sales reps sending bulk messages), “What is an email bounce back?” They’ll likely describe it as a wind before a summer hurricane – a sign of an approaching disaster.
And it is really so. Frequent bounces make your account more vulnerable to SPAM filters. Further on, this can tarnish your sender reputation and hinder email deliverability. For businesses relying on email outreach, it signifies a severe threat to their communication with potential customers.
How to handle email bounces
Email bounce backs are preventable. Below, I’ll provide particular strategies that will help you avoid this problem. Moreover, with modern outreach platforms like Snov.io, you can effectively handle bounce-back issues with minimal effort.
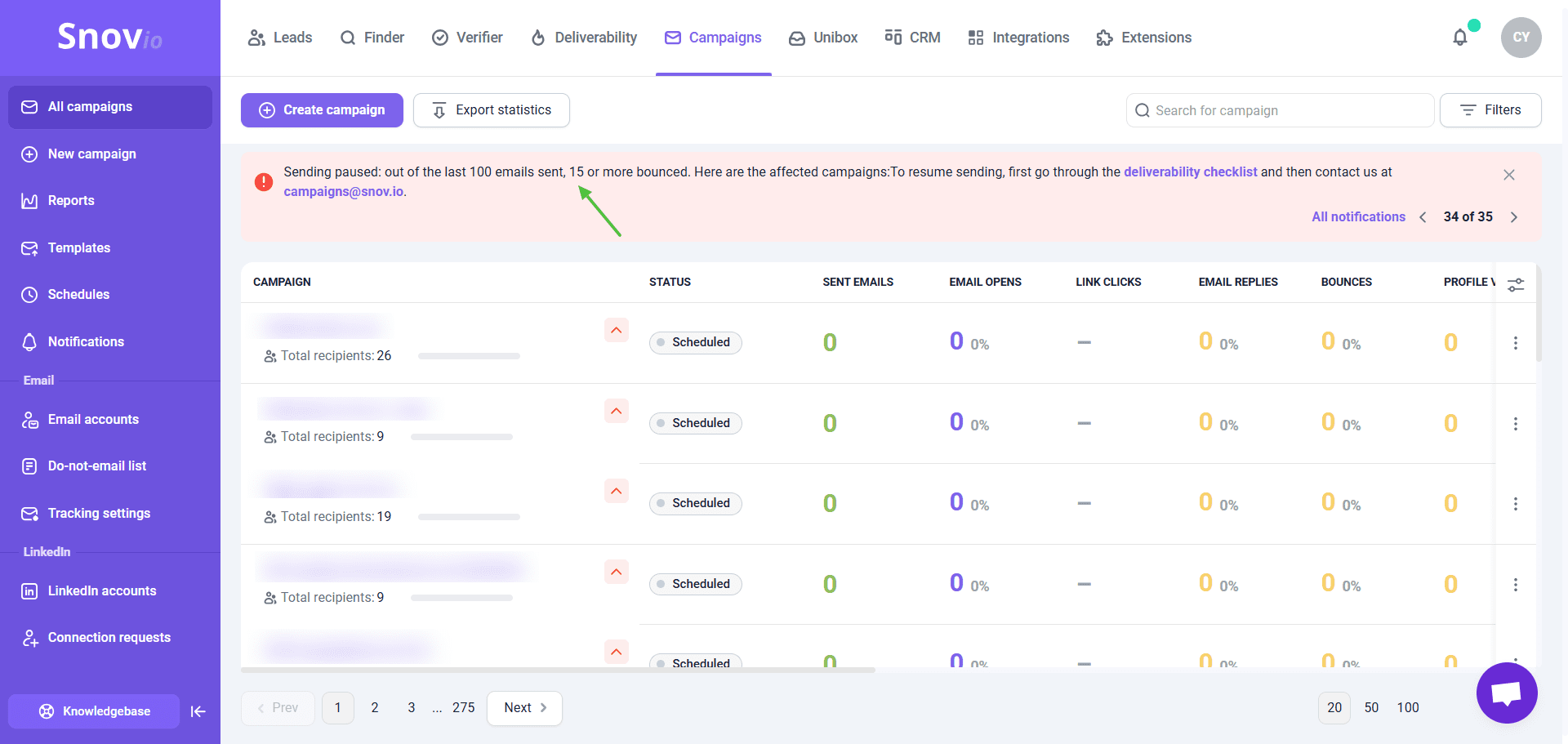
Snov.io automatically detects bounced emails in active campaigns and pauses the sequence if your bounce rate for the last 100 messages hits 15%.
Meanwhile, Snov.io Email Verifier carefully analyzes email addresses on your list, determining which ones are valid and which ones are gibberish, including catch-all addresses, disposable, or free email domains.
Below, I’ll share detailed tips on how to prevent bounce backs and improve email deliverability with Snov.io.
Types of email bounces
Typically, marketing experts differentiate between two types of email bounces.
What are soft bounces?
Soft bounces result from temporary issues that can be easily fixed. Most email services try to resend messages after encountering a soft bounce.
Common reasons that cause soft bounces include:
- A full recipient inbox
- An out-of-office status on the recipient’s email account
- A recipient’s email server being down or offline
- An overly large message
- Greylisting used by some email services
With soft bounces, once the issue is resolved, you’ll be able to send your campaigns as usual.
|
Sending emails that receive auto-replies, like out-of-office or vacation notifications, typically doesn’t result in an actual bounce. |
When people with professional email accounts are on leave or vacation, they often set up auto-reply messages informing senders of their temporary absence. In such cases, you might receive a “Vacation/Auto-Reply” message.
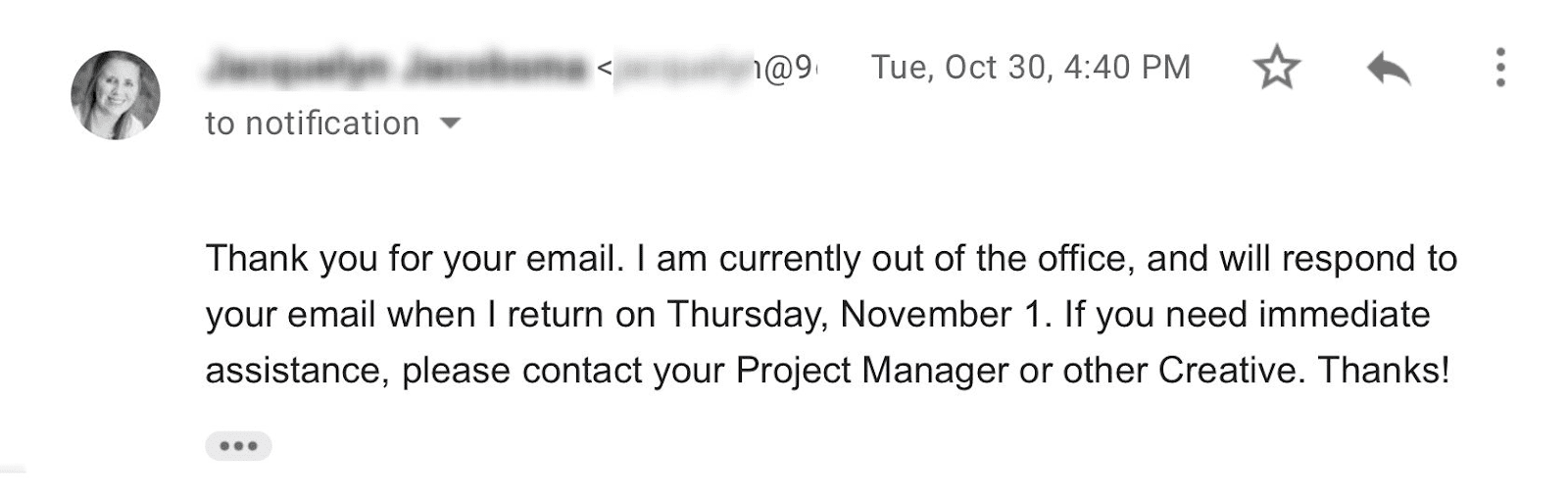
Technically, in this scenario, your email isn’t truly “bounced” because it has been successfully delivered to recipients. They will see your message as soon as they come back. However, if you consistently face a similar auto-reply for an extended period, it might be wise to remove that contact from your list.
What are hard bounces?
Hard bounces take place when your email can’t be delivered to an address permanently. Unlike soft bounces, hard bounces are a serious problem. Whenever you encounter any of these issues, resolve them immediately; otherwise, your email deliverability is at risk.
Typical causes of a hard bounce are as follows:
- Sending to an invalid recipient email address (fake, misspelled, or non-existent)
- Sending to role-based addresses (info@, support@)
- Invalid recipient’s domain (disposable or non-existent at all)
- Email address blocked by the recipient’s service provider (e.g., your domain or IP is blacklisted)
- Authentication issues on your part (e.g., missing MX records)
Hard bounces require deeper fixes before your campaigns can get through.
Now, let me share some expert insights on how to identify both types quickly.
How can you determine which bounce type it is?
To understand what bounce type you’re dealing with, refer to the SMTP error code that usually accompanies an email bounce back message.
If this code starts with the number 4, it indicates temporary delivery issues, i.e, soft bounces. Hard bounces typically begin with the number 5, signifying permanent issues.
I’ve made a table with the common SMTP error codes for soft bounces vs hard bounces so you could quickly identify what has caused your delivery issue:
| Soft bounces | Hard bounces | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Error code | Meaning | Error code | Meaning |
| 421 | Service temporarily unavailable | 550 | User not found, invalid email address, or message rejected due to spam reputation |
| 450 | The recipient’s mailbox is unavailable or temporarily full | 551 | Non-existent domain |
| 451 | The recipient’s server uses greylisting (temporary rejection) | 552 | The recipient’s mailbox is full |
| 452 | The recipient’s inbox is full and can’t receive more emails | 554 | Connection refused due to being blocked by the recipient’s server |
Now, let’s move on to some practical steps you can take to reduce your email bounce rate.
Why are your emails bouncing back: top reasons and solutions from Snov.io
In this part, we’ll talk about why you might get bounce back emails in more detail. I’ll unveil 10 reasons for bounces and provide the best solutions for each bounce case. On top of that, I’ll share specific examples of how you can handle issues faster and more efficiently with Snov.io tools and features.
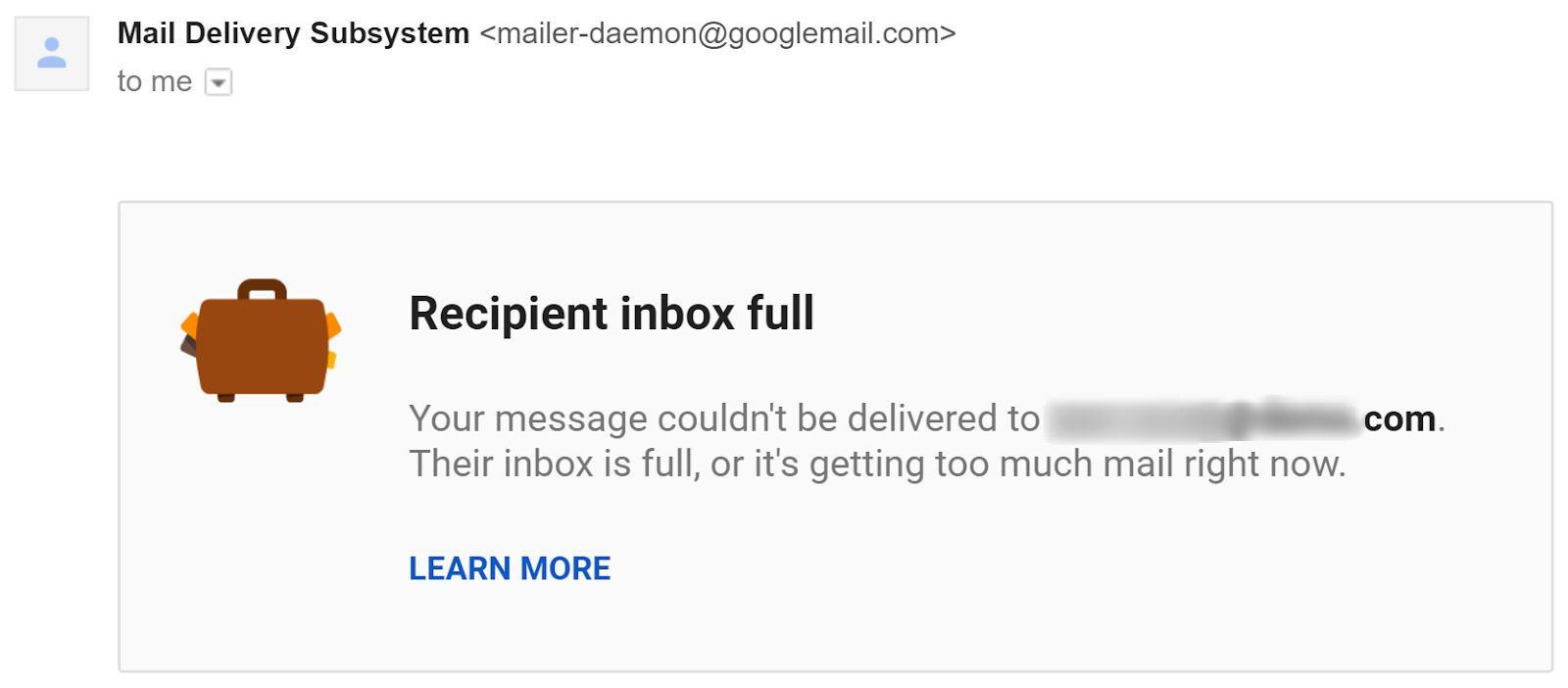
Reason #1. A recipient’s mailbox is full
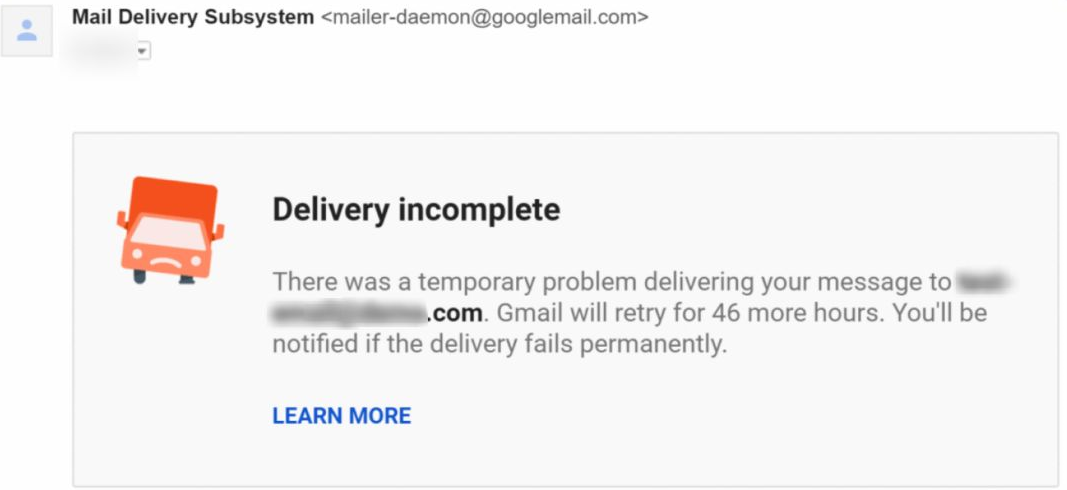
Each email provider offers a limited storage capacity. If a person you’re reaching out to has exceeded their storage limit, they can’t receive new messages. Consequently, you’ll receive an email bounce back when trying to send a message to them:
Solution:
As this bounce back email indicates a temporary issue, you can either wait or take alternative steps:
- Reach out to the recipient through other means, e.g., social media.
- Inform them about the problem and politely ask to free up some space.
If you’re sending messages in bulk, you can use Snov.io’s LinkedIn automation tool to connect with prospects on this social network. Provided you’ve got prospects’ profiles, it won’t be hard to do. Just add alternative LinkedIn actions to your sequence:
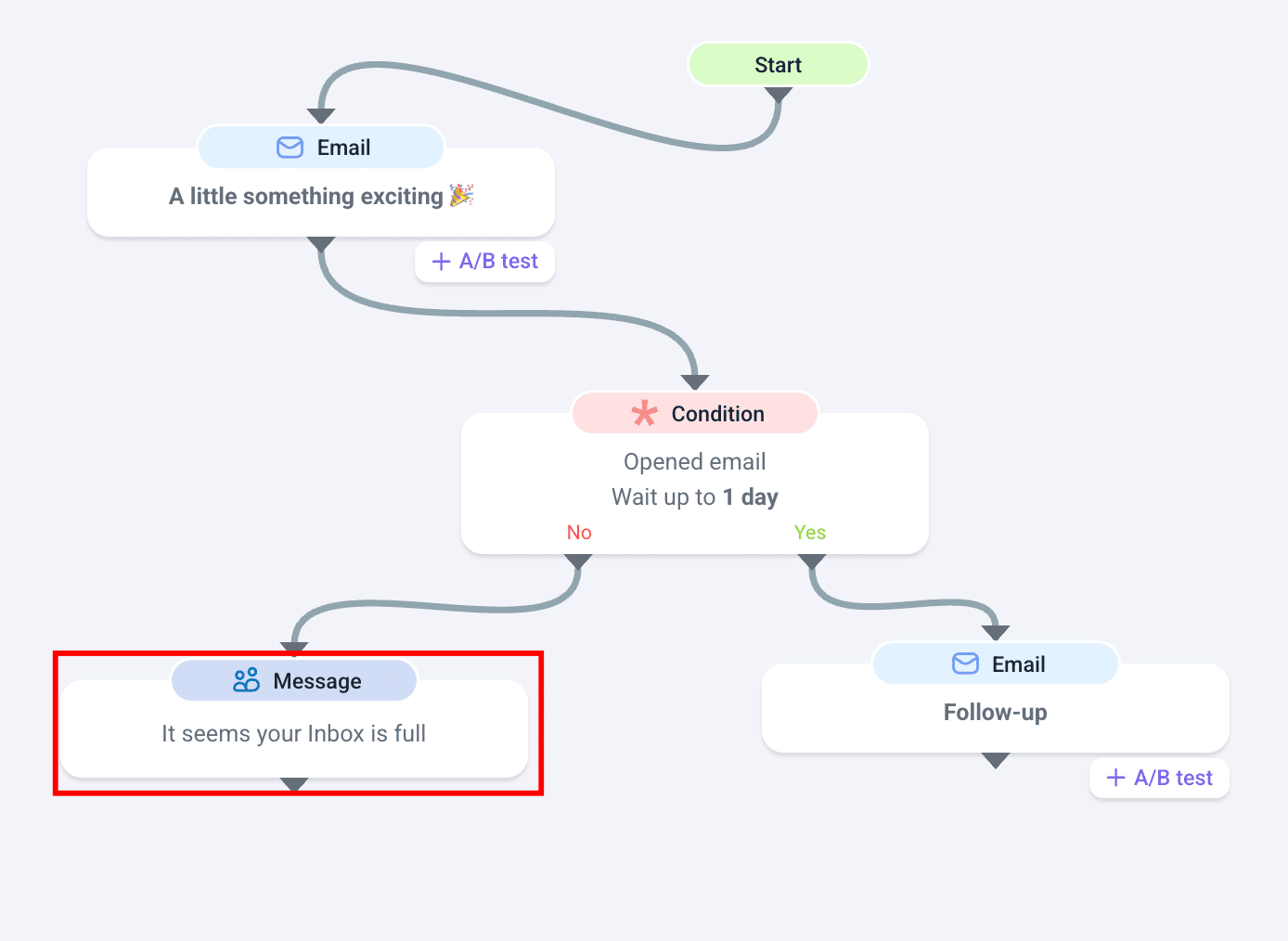
And here’s a ready-made template for your LinkedIn message:
Hi [Name],
I tried reaching out to you via email, but it bounced back because your inbox is full. Since we’re connected on LinkedIn, I thought I’d try to reach out to you here.
I saw your company is planning to change its outreach strategy for the next year. What if [Company Name] could help you [Describe value] and [Describe a real result they can achieve]?
Would you like me to send a quick overview of your positive changes?
If it’s more convenient for you to communicate via email, would you be so kind as to make some space available so I can contact you there?
Best regards,
[Your Name]
Reason #2. A recipient mail server is down or offline
Sometimes your recipients might experience server issues: it could crash, become overloaded, or be under maintenance. This situation typically leads to a soft bounce, resulting in your getting a bounce back email:
Solution:
- Wait until the problem with a recipient’s server is resolved.
- If you need to urgently connect with the recipient, consider alternative means of contact.
Remember that multichannel campaigns can be handy, especially for bulk outreach.
Reason #3. Your message is too large
Many providers set size limits on incoming emails. If your message is too big, it might result in a soft bounce. Additionally, some service providers don’t allow images or huge attachments, so if your message isn’t solely text-based, you may get an email bounce back.
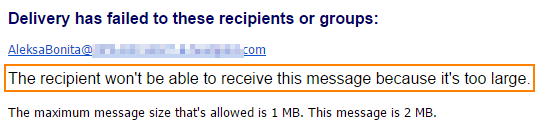
Solution:
- Enhance your email content to ensure it remains within optimal size limits.
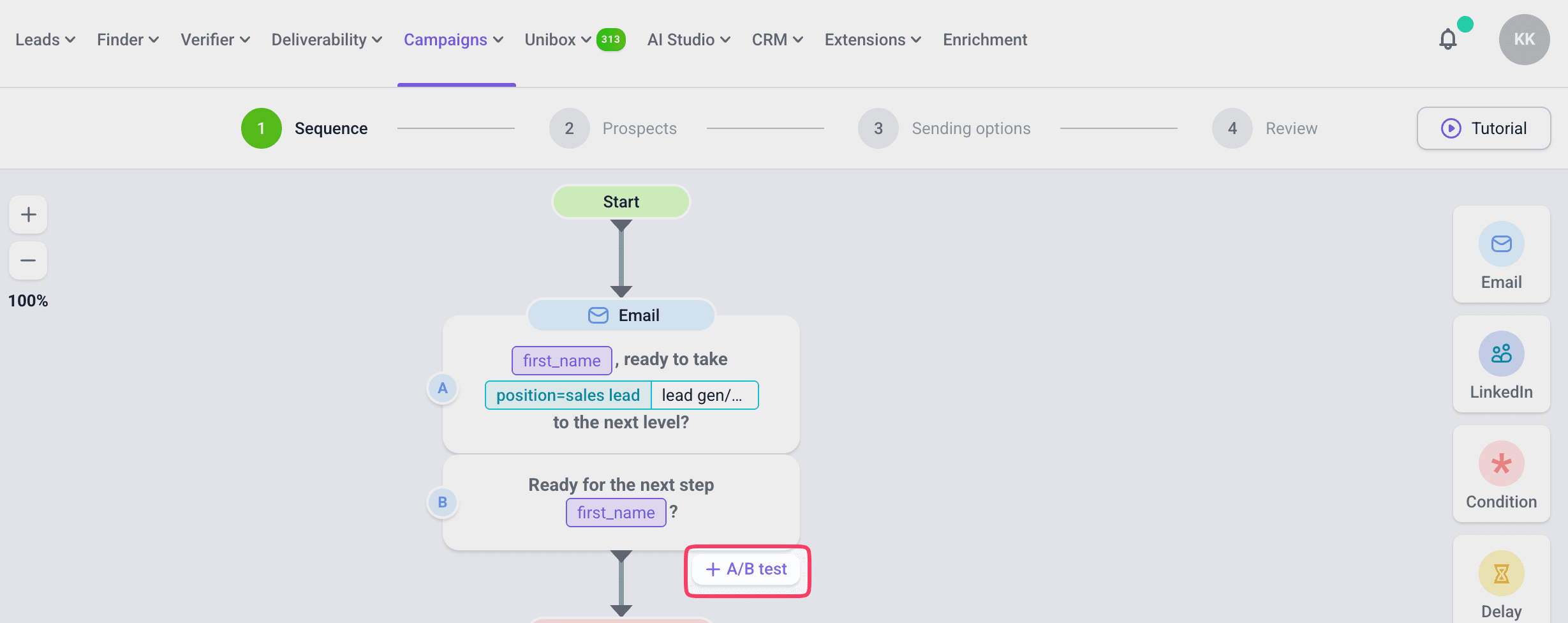
- A/B test your campaigns to determine preferences between longer and shorter versions, as well as between HTML and plain text formats.
In Snov.io, for example, you can add A/B testing to any step of your sequence, including up to 15 variations per step.
Results can be easily monitored in your campaign statistics, so you can always see which variations perform best.
To get accurate A/B testing results, test only one thing at a time and with similar ICPs, whether it’s your subject line, the use of HTML vs. plain text, or email length. Testing multiple elements at once makes it difficult to determine what actually influenced deliverability.
VP of Sales at Snov.io
Reason #4. Your email is greylisted
Greylisting is a unique spam filtering method that temporarily delays email deliveries from unknown senders, often for a duration of up to 900 seconds. During this period, a legitimate SMTP server API will attempt to resend a delayed message multiple times until it gets accepted.
When you encounter a greylist, you might see a bounce back email code appearing in the NDR:
Solution:
- Wait for an automatic retry.
- If your message is sensitive, and contacting a recipient is a critical issue, consider alternative means of outreach.
- Ask the recipient to whitelist your email address or domain. This will exempt your campaigns from the greylisting process and allow them to be promptly delivered.
Has greylisting become a frequent problem? Something may be wrong with your authentication.
Reason # 5. You haven’t authenticated your account properly
If your Domain Name System (DNS) records are missing or misconfigured, receiving servers may reject your message, especially if their spam filters are strict.
In such cases, you’ll receive a bounce-back email explaining why your message wasn’t delivered. Such an email often comes with an SMTP error code like 550, 554, or one related to authentication failures.

Source: Mailmodo
Solution: Set up DNS records. Here’s how you can do it step by step:
Step 1: Access your domain’s DNS settings
Log in to your domain account on the platform where you’ve purchased it and open DNS settings to get started.
Step 2: Add an SPF record
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) authorizes specific servers to send campaigns on your behalf. By default, the SPF record has this format:
|
v=spf1 include:spf.example.com ~all |
To add this record, create a new TXT record. In the “Name” field, enter @ or your domain name. Then, in the “Value” field, insert your provider’s SPF value instead of spf.example.com. Once done, save the changes and wait 48 hours for them to take effect.
Step 3: Set up a DKIM record.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) verifies that your email content hasn’t been altered in transit.
To set up this record, generate a DKIM key pair in your service provider’s dashboard. You’ll receive a host name and a public key. Next, create a new TXT record in your DNS settings, using the provided host name (e.g., google._domainkey) and pasting the public key into the “Value” field.
Here’s a value example, where everything that goes after p is your public key:
|
v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA7vPxh6zZ7nBLj1QUXGEXAMPLEKEY… |
Now, save the changes to activate DKIM authentication for your domain.
Step 4: Add a DMARC record
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) tells servers how to handle failed SPF/DKIM checks.
To add this record, go to DNS settings and create a new TXT record. In the “Name” of “Host” field, enter dmarc.userdomain.com, where userdomain.com will be replaced with your domain name. In the “Value” field, add your DMARC policy and save the changes.
DMARC records follow a standard format:
|
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto: your-email@yourdomain.com. |
Everything that goes after p refers to DMARC policy. It is recommended to change the policy from default p=none to p=quarantine or even p=reject for stronger domain protection.
Replace the email address after mailto: with the real address you created for reports and save this record.
Step 5: Set up an MX record
MX (Mail Exchange) directs email traffic to your provider’s mail server. If it is missing, it indicates that there are no servers to receive your messages, resulting in bounces.
To add this record, select the MX record type in DNS settings, enter @ or your domain address, and the MX value given by your provider. Set the priority depending on how many MX records you already have and the time to leave (default or 3600 seconds). Finally, save this record and wait for 48 hours.
Other records you might need to set up:
- rDNS / PTR Record for confirming your sending IP matches your domain (helps avoid spam flags)
- A-record (Address Record) for connecting your domain to a specific IP address
Though it’s not an absolute must-have, experts often advise setting a custom tracking domain to replace generic tracking links with your branded domain.
→ Set up a custom tracking domain easily with this guide.
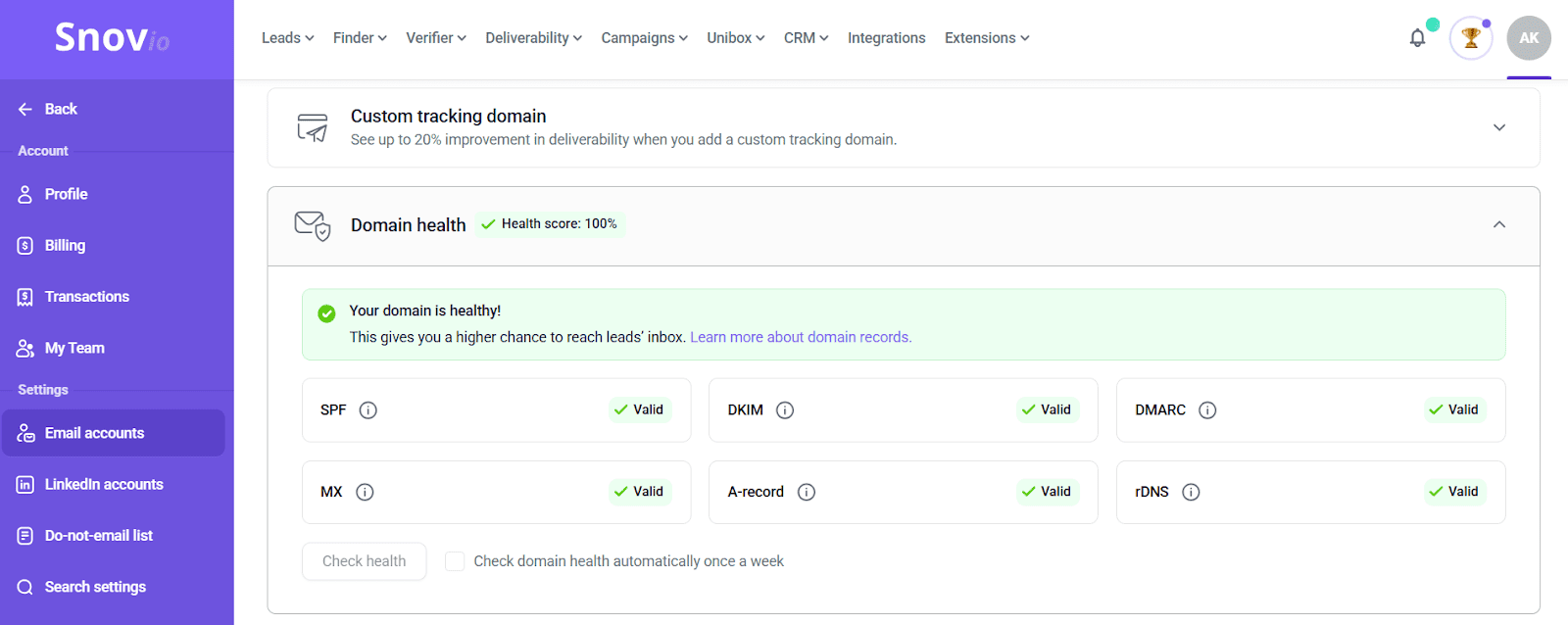
Step 6. Verify your records
Once you have set up all records, ensure they are well-configured and optimized for maximum inbox placement. You can easily do it with the Email Deliverability Test from Snov.io.
Apart from checking authentication records, this tool provides personalized tips on how you can enhance your campaigns for higher sender reputation and deliverability.
→ Read our post for a more detailed guide on how to set up DNS records.
Reason #6. A recipient’s domain doesn’t exist
Similar to the previous issue, the Mail Transfer Agent might fail to deliver your message if it can’t find the destination email domain in the DNS.
This problem occurs when a recipient’s DNS records are either misconfigured or not properly set up, which causes the server to be unable to locate the domain. Alternatively, the domain itself may no longer be in use.
Solution:
- Send a test email to a recipient from another service provider to see if this issue persists.
- Check your MX records.
- Try to contact a recipient through alternative means (if possible), asking them to check their domain settings.
If a problem is on a recipient’s side, you can agree on how you’ll communicate until the issue is resolved.
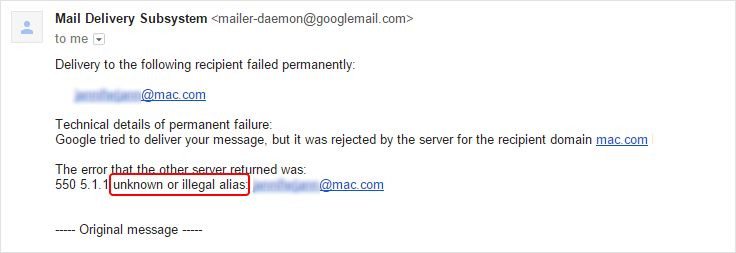
Reason #7. A recipient’s email address is invalid
Hard bounces, as you remember, might happen if the person you’re trying to reach no longer owns their account (e.g., they left the company), they’ve mistakenly given you an incorrect email address (e.g., while filling in the subscription form on your landing page), or simply because there might be a typo in their address.
In any of these cases, you’ll get a bounce back email communicating the following:
This problem may cause real damage to your sender reputation.
Solution:
- If you are sure the recipient’s address exists, check it for possible typos, unwarranted spaces, or special characters.
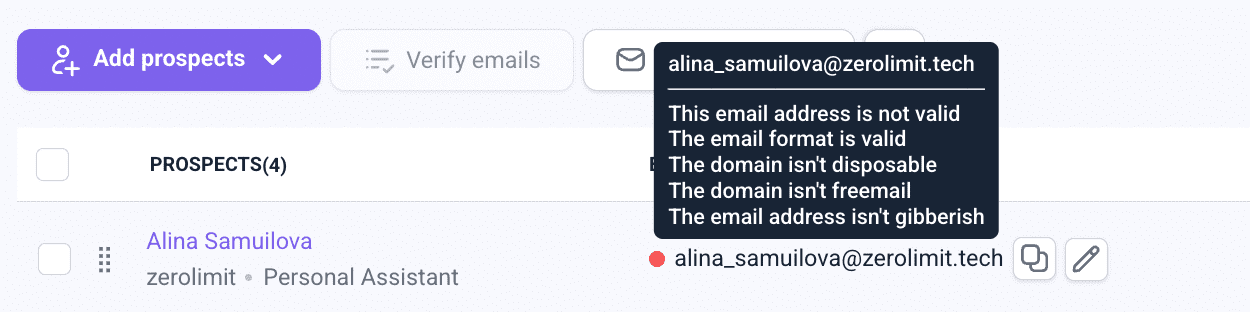
- If you hesitate, verify that this address is valid.
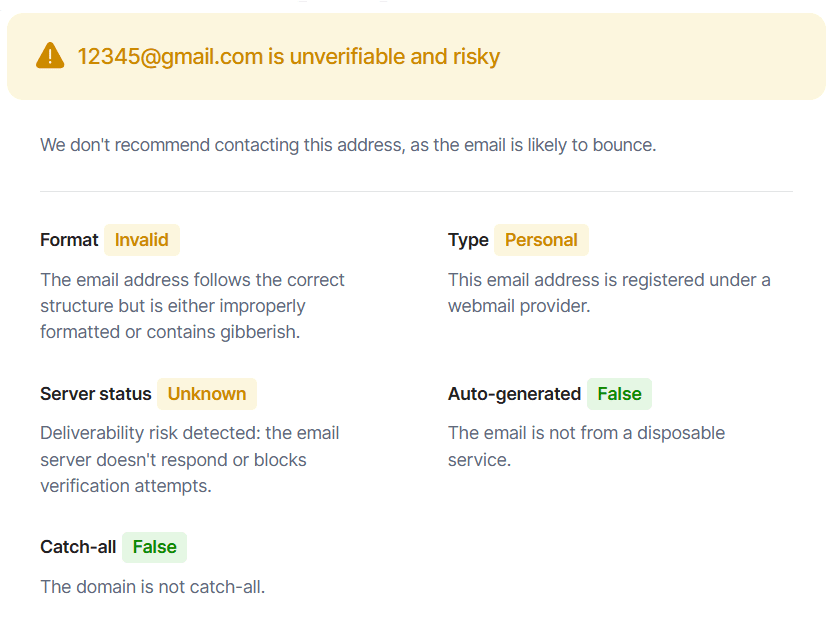
With Email Verifier, you can do instant verification for free.
Using this service, you’ll receive full information about the address you’re checking. You can instantly see if it’s valid, how the server responds, what type of address it is, and get a data-driven recommendation whether it’s safe to send.
For extensive lists, you can verify addresses in bulk. With Snov.io, this process will take you just two simple steps:
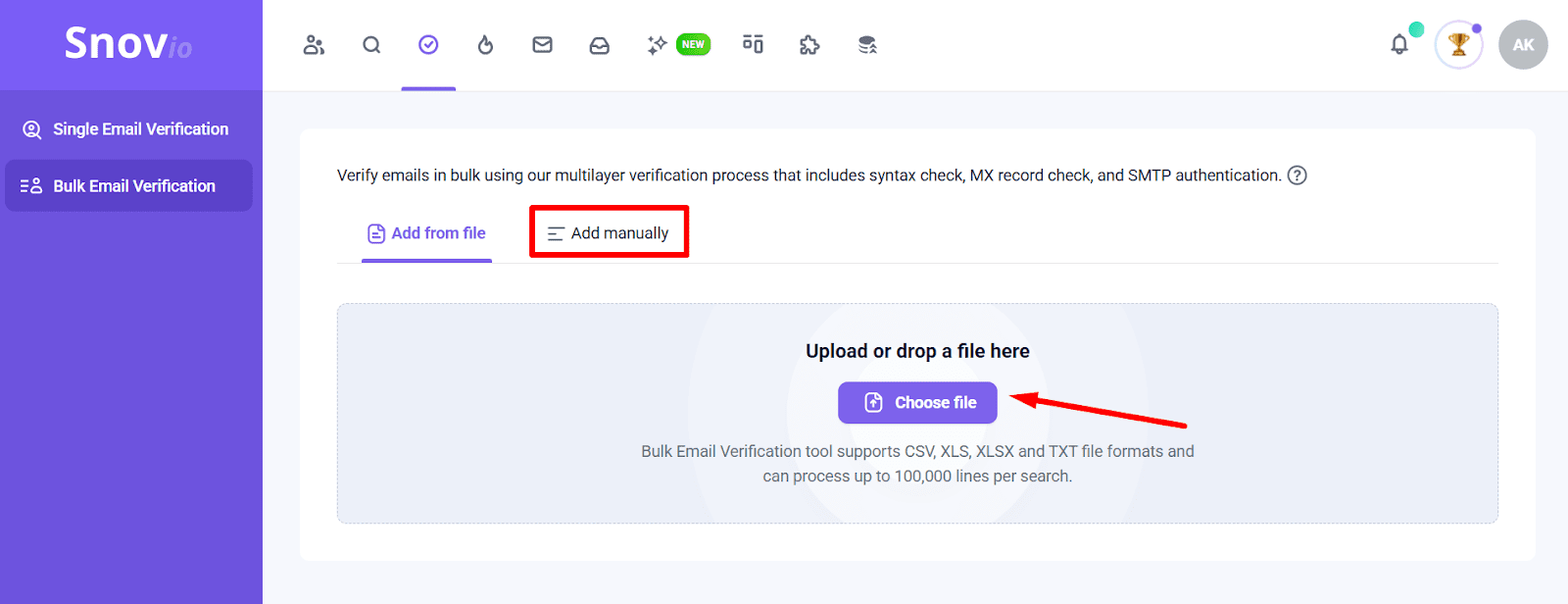
Step 1: Upload your list
Log in to your Snov.io account and go to the Bulk Email Verification page. Click on ‘Choose file’ and upload your contact list in any of the supported formats.
You can also manually add all addresses you want to verify. To do so, click the ‘Add manually’ tab and enter your contacts one by one to check them in scope.
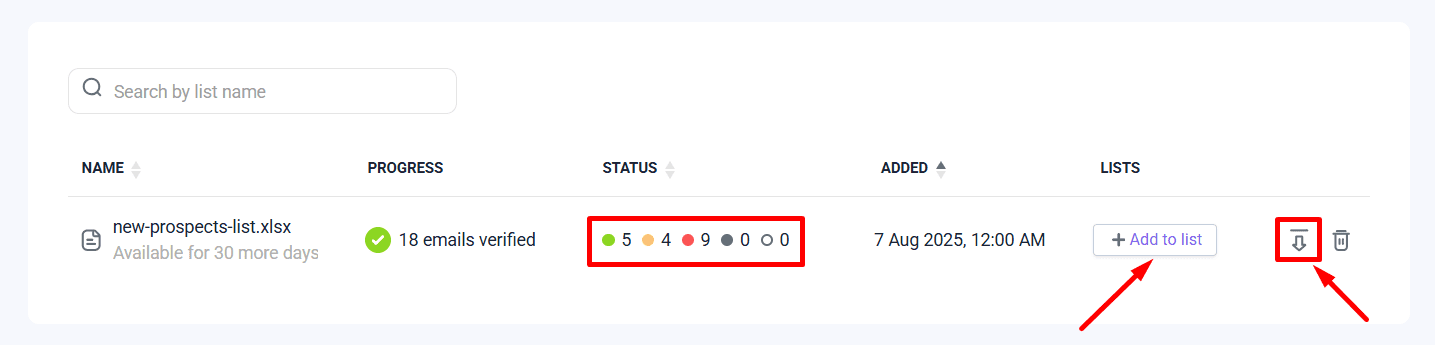
Step 2: Get your contacts verified
After you upload your list or add contacts manually, click ‘Verify’ to start checking. Once the verification is complete, you’ll see the verification status of all email addresses.
Invalid addresses are marked in red, and risky ones are marked in orange. Green indicates valid contacts, while unverified addresses are displayed in grey.
Step 3: Filter contacts
Pick those addresses that turned out to be invalid for further spellcheck (if you are sure they belong to real people). If not, remove them from your list without delay to protect your sender reputation and avoid the email bounce back problem.
Now add valid contacts to the existing list or click the Export button to download and save them for further use.
Reason #8. Your email address is blocked
Your messages may also bounce back if a receiving server has blocked your email. This acts as a “red light,” stopping your campaigns from reaching the intended inbox, while you receive a bounce back email in return:
As a rule, such a bounce occurs when the address you’re sending to is associated with large corporations, government entities, educational institutions, and similar establishments.
These organizations often have strict email policies, potentially blocking all incoming messages that are not part of their internal network.
Solution:
- Find alternative means of contacting these recipients.
- Ask them how you can become a part of their email network, so your messages are welcomed.
Alternatively, you can agree on how you’ll communicate with recipients further using other channels.
Reason #9. Your IP address is blocked
If servers detect any suspicious activity originating from your end, your IP may be blocked, preventing your messages from being delivered and resulting in a bounce-back email.
This often happens if you’re using a shared IP address (especially if you rely on free providers like Gmail, Yahoo, Zoho, and Outlook for outreach). In this scenario, if any shared user launches a spammy campaign, other users with shared IP addresses (including you) will be affected. Your domain and IP address may be blacklisted or blocked.
Solution:
- Use a specialized checker to see if your domain and IP address are blacklisted: Spamhaus, Barracuda, Proofpoint, and others. This email blacklist guide, prepared by our outreach experts, explains how to do it step by step.
- Switch to a dedicated email address if possible and don’t rely on a free provider for sending messages in bulk.
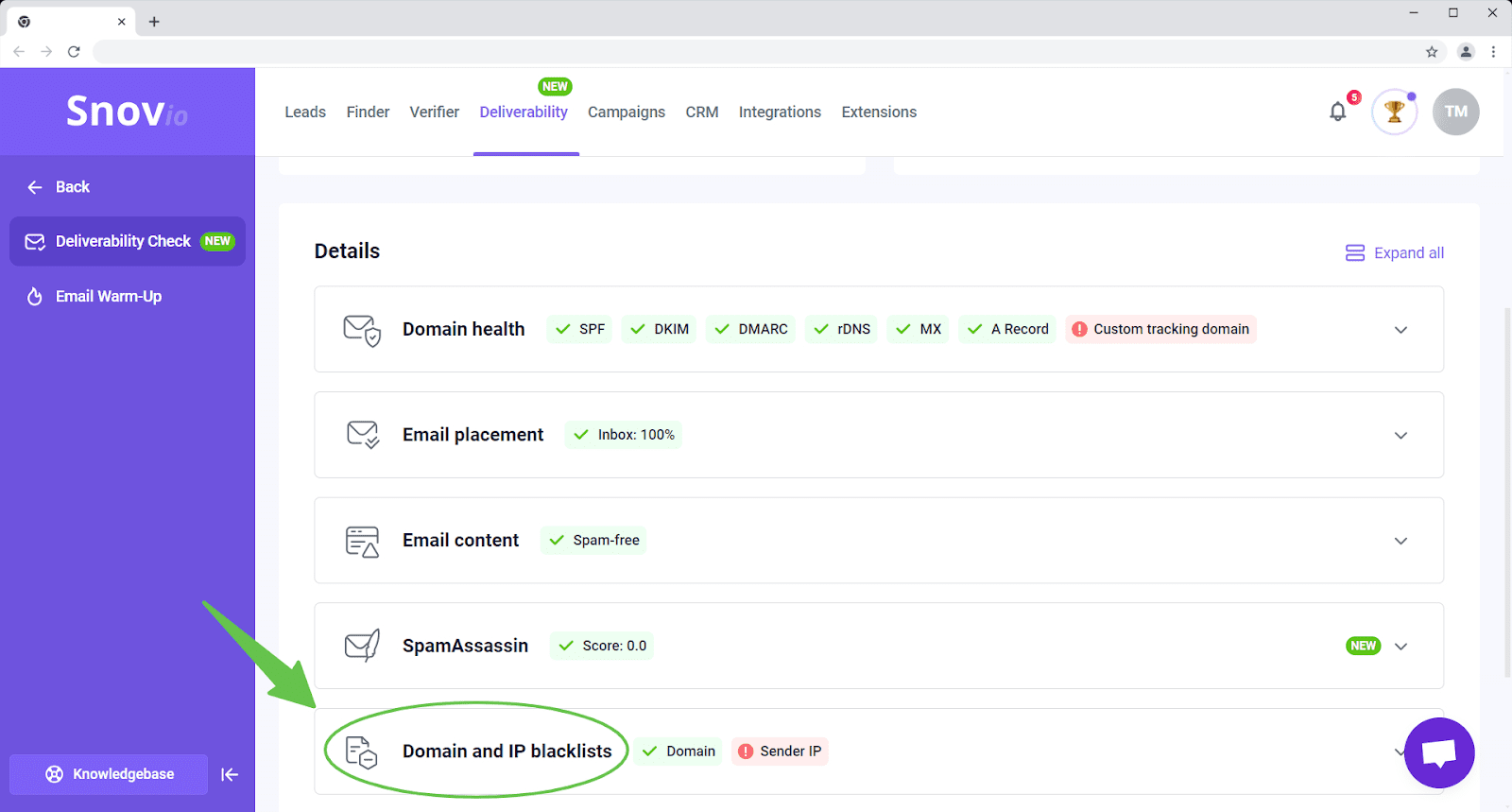
You can run the Blacklist test integrated into the Snov.io Deliverability Check. Within seconds, you will see if your domain or sender IP has been found on any blacklists.
Besides, Snov.io offers a powerful Email Warm-up to help you gradually prepare your account for bulk sending. This tool simulates natural sending and receiving patterns, automatically increasing your email volume in a mild and safe way.
You can also try a Premium warm-up, commanding Snov.io to exchange emails exclusively with business and corporate mailboxes. Plus, you can target particular providers, like Outlook or Gmail, to overcome bounces caused by domain-specific issues.
Reason #10. You have a low sender reputation score
Bounces you have already accumulated may already be a reason your sender reputation is down. As a result, you’re becoming more vulnerable to SPAM filters and might get even more bounce backs.
Solution:
- Monitor your current bounce rate and sender reputation score to see how you can improve your performance.
- Follow safe sending limits to avoid triggering spam filters or exceeding provider thresholds. Our experts recommend staging within the daily sending volume at 50–100 emails per account to avoid delivery issues.
- If you want to send in large volumes, consider distributing your outreach across multiple email accounts.
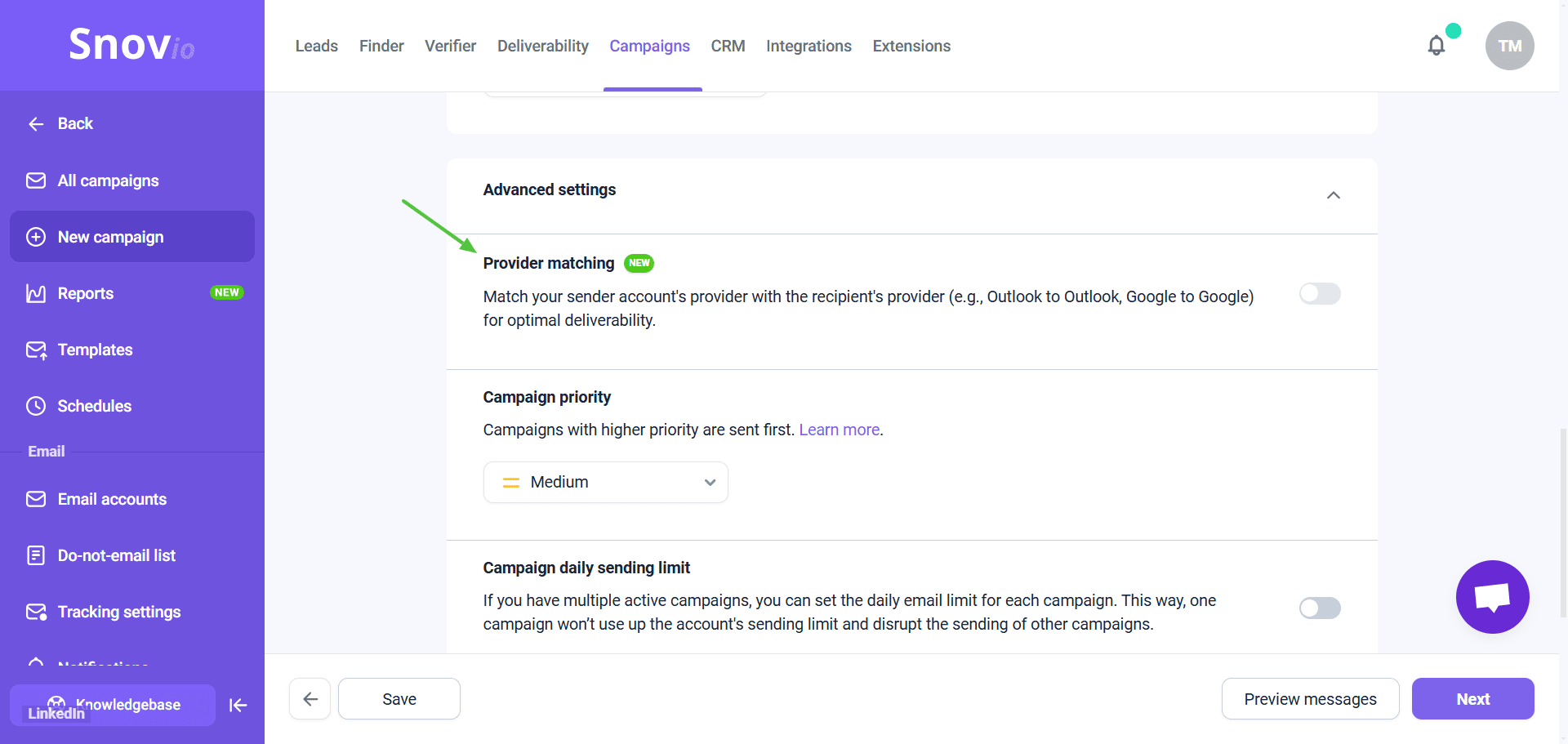
Owing to the Mailbox rotation feature from Snov.io, for instance, you can send more messages in one campaign and diversify mailboxes for better efficiency. What’s more, Snov.io automatically detects the match between your account and your recipients’ providers during sending.
That means your Gmail emails get delivered to Gmail recipients, while messages sent from Outlook magically go straight to Outlook users.
How to calculate your email bounce rate
To understand which email bounce rate is okay and when it’s high time to fix bounce backs, let’s figure out how to calculate it.
It’s not hard math to calculate bounce rate on your own:
- Count all bounced emails: This is the total number of emails that didn’t successfully reach the recipient’s inbox for a specific period.
- Count the total sent emails: This represents all the emails you’ve dispatched in the same period.
- Divide and multiply: Divide the number of bounced emails by the total sent emails. Multiply the result by 100 to get the percent value.
The good news is that your marketing outreach tool calculates the email bounce rate for you, as a rule, so you won’t do it manually 🙂
Anyway, let’s look at how the calculation runs:
|
Imagine you’ve sent out 10,000 campaigns. Out of these, 240 didn’t make it to the recipients. 240 / 10000 = 0.24. ‘0.24’ means that for every email you sent, 0.24 bounced. Now, multiply that number by 100 to express it as a percentage. 0.24 * 100 = 2.4% So, your bounce rate is 2.4%. |
But how do you understand whether it’s a good bounce rate or not?
Let’s address benchmarks.
What is an acceptable email bounce rate?
It all depends on the industry. The average benchmarks for soft and hard bounces across various industries, based on Brevo’s 2025 report, look like this:
| Industry | Soft bounce rate | Hard bounce rate |
|---|---|---|
| Culture and Arts | 2.62% | 0.08% |
| Travel and Tourism | 3.21% | 0.09% |
| Public administration | 2.51% | 0.10% |
| Hospitality and Leisure | 3.05% | 0.11% |
| Retail | 2.96% | 0.13% |
| Real Estate | 3.39% | 0.13% |
| Education | 2.92% | 0.14% |
| Telecom and Media | 3.94% | 0.15% |
| Energy and Utilities | 3.44% | 0.16% |
| Healthcare | 3.16% | 0.18% |
| Manufactoring | 3.19% | 0.18% |
| Professional Services | 3.85% | 0.20% |
| Construction | 4.19% | 0.21% |
| Ecommerce | 6.45% | 0.22% |
| Finance | 4.40% | 0.24% |
| Technology | 3.94% | 0.32% |
| Marketing and Advertising | 8.65% | 0.34% |
The average rate across industries is 3.6% for soft bounces and 0.19% for hard bounces. Therefore, the acceptable benchmark for email bounce rate is 1,89-2%. If your email bounce rate exceeds this number, it’s time to focus on improving this metric.
How to reduce your email bounce rate forever: a recommended checklist
Above, I shared how you can handle bounces depending on what caused them. In this chapter, let me share general tips for keeping your email bounce rate under control.
Maintain your email list hygiene
Keep your email list clean: remove invalid, outdated, and inactive email addresses, which will most likely bring you bounce backs soon. Use Snov.io’s Verifier to check if addresses are valid before reaching out. This can save you from sending to addresses that are certain to bounce.
Avoid sending campaigns to purchased lists
I strongly recommend that you never try purchasing email lists. These lists are likely to contain invalid or disengaged contacts, which can result in high bounce rates for you in several months or weeks.
🔎 Expert tip
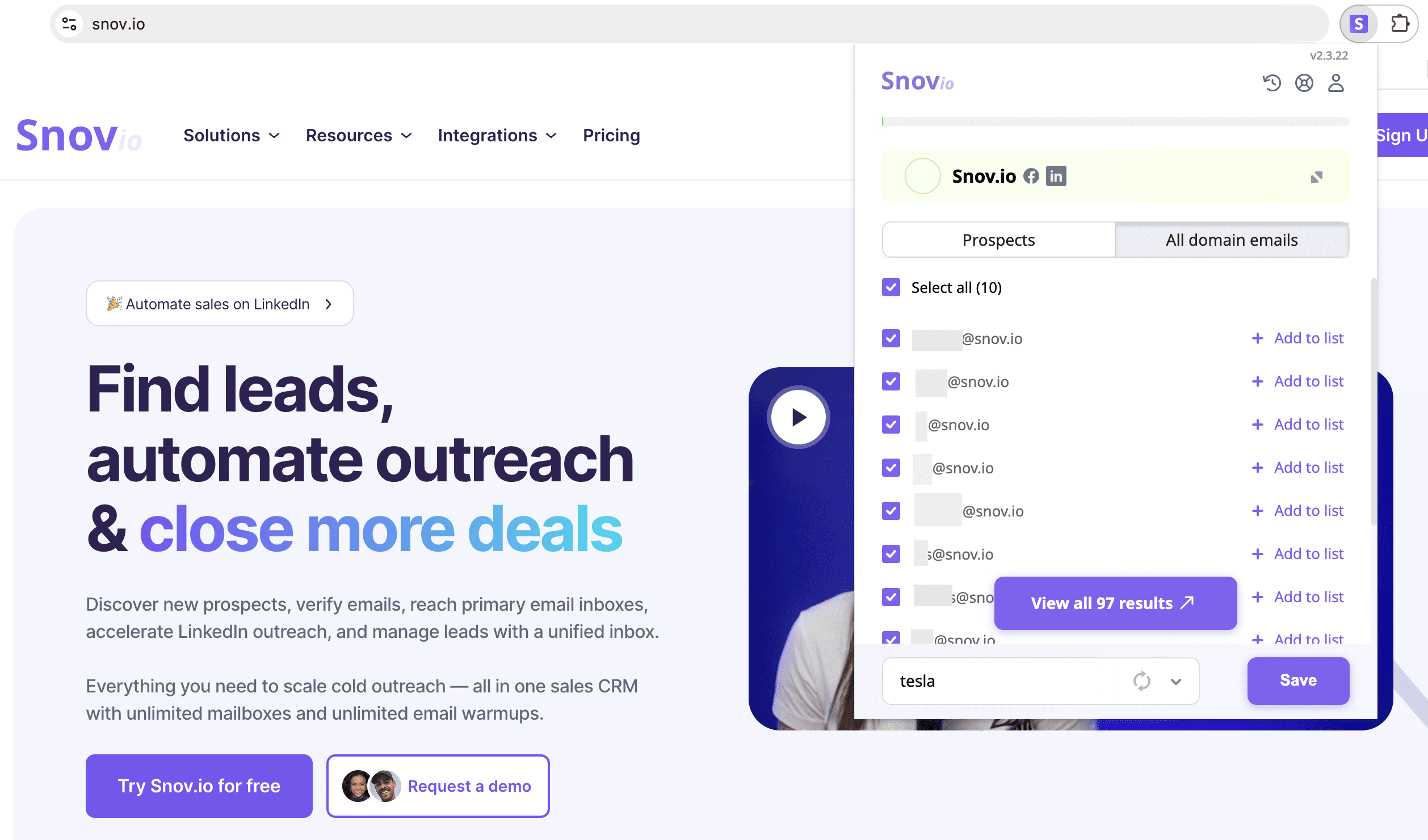
If you’re building your outreach list from scratch, always use reliable and trustworthy tools to collect addresses. With Snov.io Email Finder, for example, you can collect high-quality leads from websites, company domains, and even LinkedIn in seconds.
The highest accuracy of search results is guaranteed: every address you find is automatically verified, ensuring bounce-free and effective outreach.
Use a double opt-in process
Encourage subscribers to confirm their email addresses through a double opt-in process (subscription form + confirmation emails). Thus, you ensure that all contacts you’ve collected are valid and owned by subscribers.
Authenticate your account
Email service providers (ESPs) check authentication to evaluate senders’ reputation. Messages that fail authentication checks may not only bounce but also trigger spam filters, affecting your sender reputation and deliverability. To avoid email bounce back messages, set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records in your domain’s settings.
Segment your list
Segment your list based on various criteria: user behavior, demographics, engagement levels, past purchases, or other relevant factors. By grouping your subscribers based on shared characteristics, you increase your chances of reaching out with highly relevant messages.
More tailored messages better resonate with your audience, resulting in a higher level of engagement. This signals to ESPs that your email content is engaging for recipients, which in turn lowers bounce rates.
Send regularly, but don’t spam
Send to your list with a certain regularity, but not excessively. If you’ve got a new account, warm it up. Start by sending no more than 20-30 emails per day and encourage your contacts to interact at any cost: open, read, click, and reply. Gradually increase your daily sending volume when you see improvements in engagement rates.
What else can you do? Activate a random, longer delay between emails (e.g., between 120 and 180 seconds). This will help you avoid spam complaints, increase engagement, and reduce bounce rates.
Avoid spammy content
Your content matters for your email bounce rate as well. Here is what you can do in this direction:
- Avoid spam-trigger words in your email content (e.g., words like FREE, OFF, DISCOUNT). They are often taken for spam or too promotional by various service providers.
- Shy away from CAPS, bolded formatting, and exclamation marks. They can signal that your campaigns are promotional or spammy.
- Do not use too many links. Otherwise, you may be suspected of phishing activity, and the receiver’s server will reject your messages, while you’ll receive bounce back emails.
- Maintain a 60:40 text-to-image ratio. Yes, HTML emails look great compared to dull, plain-text messages. However, HTML format is often associated with promotional marketing campaigns. So, you’d better maintain a mixed ratio between the text and HTML images for your campaigns.
By following these recommendations, you can help prevent your emails from being flagged as spam, lowering your chances of getting an email bounce back.
Test deliverability, sender score, and spam rate before sending campaigns
Perform regular email deliverability, sender score, and spam rate checks to identify potential issues with delivery and spam. Ensure your sender score is 80 or higher. You can check it on a Sender Score platform.
If tests show poor deliverability, sender score, or blacklisting problems, pause your active campaign and start a warm-up process for the email account that sends it.
Use multiple accounts for bulk sending
If your campaign targets thousands of leads, create additional sender accounts to avoid exceeding the limits. Even if you’ve got up to 10 accounts, it won’t be too much. Remember, sending more than 100 messages daily may cost you unwanted bounces and other deliverability issues.
Monitor your bounces regularly
Don’t delete bounce back messages. They help you understand which type of bounces you’ve received and how to handle the situation accordingly.
For your convenience, I’ve summed up the most common bounce-back cases, categorized by SMTP error numbers. Each case includes a clear explanation, actionable solutions from our expert team, and the relevant Snov.io tools you can use for fixing bounce issues.
| Bounce back email | Reason/Meaning | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Soft bounces | ||
| SMTP 421 (Server Temporarily Not Available) | The mail queue is overloaded. | Resend the email at a later time. You can use the Snov.io Cold Email tool to automate retries. |
| SMTP 421 (Temporary Rejection. Reverse DNS for “IP” failed) | Couldn’t identify the PTR record. | Verify the sending IP’s reverse DNS setup before resending. Run the free Deliverability test or check the domain health in your Snov.io account. |
| SMTP 452 (“fromemail” sender rejected. Too many messages for this connection ERR034) | Exceeded sending limits. | Send from another account or in batches. To avoid this issue, distribute volume across multiple accounts, using Mailbox rotation in Snov.io. |
| SMTP 452 (“toemail” requested action aborted: try again later – GL/GL) | Temporary failure due to greylisting. | Retry after delay. You can schedule your retries in Snov.io to get rid of repetitive tasks. |
| Hard bounces | ||
| SMTP 550 (“fromemail” max messages per session) | Exceeded email-sending limits. | Resend the email later. Check Snov.io recommendations for daily sending limits in your account settings and follow them in your campaigns to stay within safe boundaries. |
| SMTP 550 (“fromemail” sender rejected) | Misformatted email address (missing @domain). | Double-check the email format. Use Snov.io Email Verifier to validate and clean your email list. |
| SMTP 550 (“toemail” recipient rejected GL/BL) | The sender is blacklisted by the recipient. | Your email address could have been blacklisted accidentally. Run Snov.io Deliverability check to identify blacklist status. |
| SMTP 550 (“toemail” recipient rejected) | The recipient’s mailbox doesn’t exist. | Remove or correct the invalid email address. Use Snov.io Verifier to detect invalid addresses before sending and prevent hard bounces. |
| Reject SMTP 550 (“toemail” recipient rejected – ERR016) | The recipient is blocked due to spam, blacklist, or email limits. | Request the sender to check server logs for precise rejection reasons. Whitelist email on the recipient’s end and try resending it. |
| SMTP 550 (“fromemail” sender rejected – ERR082) | The sender is blocked due to spam, blacklist, or limits. | Similar to ERR016. Check server logs and try whitelisting the email address. Use Snov.io’s Warm-up tool to build a strong sender reputation. |
| SMTP 550 (“fromemail” sender rejected – ERR081) | Domain is blacklisted. | Attempt to get the domain whitelisted on the recipient’s end. |
| SMTP 550 (“fromemail” suspect invalid mailer domain, please check your DNS records – ERR006-009) | Issues with DNS Records of the ‘From’ email. | Confirm and correct DNS records. Ensure all records are updated. Try whitelisting the email address and resend your message. |
| SMTP 550 (“toemail” recipient is invalid – ERR010-014) | Issues with the ‘To’ email address or its DNS. | Instantly check the address with Snov.io Verifier or ask the recipient to confirm it. |
| Error 550: You have reached the maximum number of messages per session. | Message limit reached for the session. | Wait and resend later. You can try multichannel outreach in Snov.io and use LinkedIn as a second platform for your outreach. |
| SMTP 552 (Remote MTA $ip: A URL contained in this message is blacklisted by Spamhaus DBL.) | The URL in the email is blacklisted. | Remove the problematic URL and resend the email. Use the Snovio custom tracking domain to track opens, clicks, and unsubscribes, ensuring a secure look for the recipient’s provider and preventing bounces. |
| SMTP 552 (virus-infected message rejected) | The message is flagged as having a virus. | Include an opt-out option and validate recipient lists. If flagged in error, report the issue. |
| SMTP 552 (virus-infected message rejected) | The sender attached a file format that is not allowed by the server (.bat .btm .cmd .com .cpl .dll .exe .lnk .msi .pif .prf .reg .scr .vbs). | Include an opt-out option and validate recipient lists. If flagged in error, report the issue. |
| SMTP 554 (Connection refused – “IP”) | Rejection based on CSI due to spam suspicion. | Check the sending IP’s reputation on Cloudmark Sender Intelligence. |
| SMTP 554 (Connection Rejected. Reverse DNS for “IP” does not exist) | Missing PTR record, perceived as spam. | Confirm PTR records and check for potential IP blacklisting. Set up your DNS records and monitor your domain health in Snov.io. |
| Reject connection SMTP 554 (rejected for policy reasons) | The sender is suspected of spam or has authenticity issues. | Check if the IP is on the Spamhaus Policy Block List and address it accordingly. Also, use the Deliverability Check tool in Snov.io and fix the issues found during the test. |
You can refer to this table whenever you need quick assistance with bounce back emails.
Key takeaways
Bounce back emails are a sign that your messages can’t be delivered at this moment. While soft bounces are a temporary issue that may be solved, hard bounces signal permanent issues like invalid emails or blocked domains.
Bounces can be and should be prevented. Here’s what you can do by accompanying your strategy with Snov.io tools:
- Send email campaigns and detect bounces instantly
- Pause sendouts automatically if issues persist
- Verify your contact lists so you can remove all invalid or risky addresses
- Check email authentication and domain health
- Test email deliverability and spam rates to identify and resolve issues promptly
- Warm up your account, preparing it for safe bulk sending
- Connect multiple accounts and rotate them smartly to keep up with sending limits
- Send multichannel campaigns catching unavailable recipients on LinkedIn.
All these and more opportunities are available on any Snov.io plan – just get on board and enjoy your bounce-less activity to the fullest!