Sales management
So now you have it — a great product with a lot of resources invested in promotion finally presented to the market. But how do you start making money on it?
Sales are what technically brings your company revenue, and the effectiveness of sales management is what sets out your corporation’s long-term survival.
What is sales management?
Sales management is the process of developing, planning, monitoring, and controlling the entire process of selling your company’s goods or services. It also concerns recruiting, training, and supervising your sales force and covers all pre-sales, sales, and post-sales activities.
Sales management components
Sales management stands on three pillars:
1. Strategy
Without having a clear strategy your sales efforts will be fruitless. To know what resources and specialists your business may require, you should set up a sales process and plan a series of activities at every stage of your sales funnel or sales pipeline. This can be done for either the whole company or in regard to individual brands, goods, or services.
A sales funnel is a powerful analytical tool, if designed with a data-first approach. It describes a single customer’s journey through 5 steps: awareness, interest, consideration, decision, and — the most desired stage for all businesses — purchase.
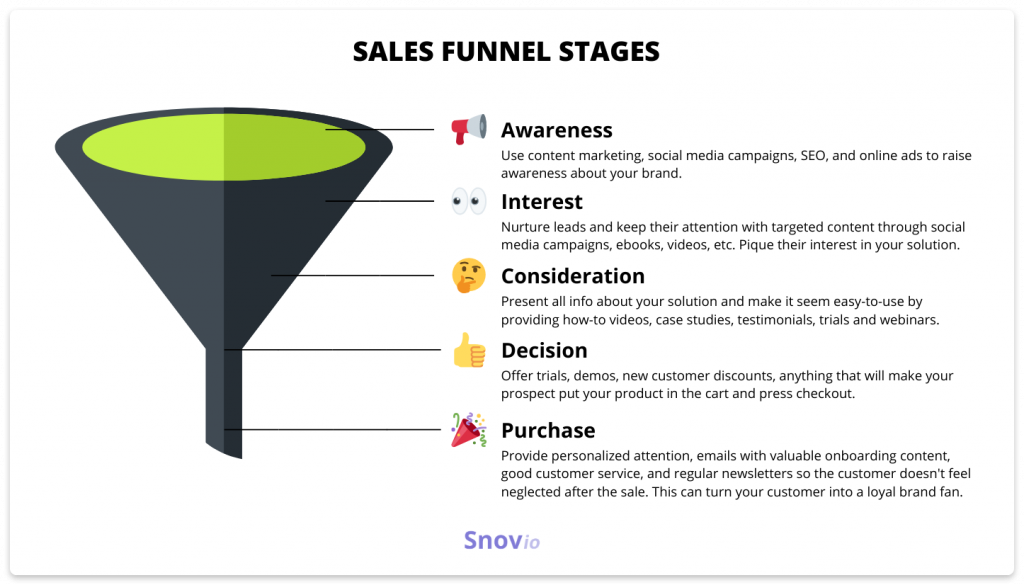
The funnel conditions sales pipeline — determined stages of reaching out to clients. It varies between companies, depending on the market type, resources owned, and business objectives. But as a rule, the pipeline has such stages as lead generation, qualification, meeting, proposal, and closing the deal.
Keeping in mind the funnel and the pipeline, you’ll be able to come up with a documented sales plan. This typically covers:
- Development goals
- Sales KPIs
- Buyer personas profiles
- People and processes
- Exact selling methodologies
- Software needed.
→ Don’t underestimate the power of automation. With the email checker tool, for example, you can ensure your team never sends marketing campaigns to inactive or invalid email addresses. Plus, skipping email verification is the number one reason for bad deliverability.

2. Operations
A sophisticated strategy isn’t worth a penny without being implemented. You need the team on paper to come true. People are the stumbling block that separates average companies from the best players in the market.
It’s not only that sales reps bring you revenue — they are your brand’s ambassadors. Salespeople directly deal with:
- Lead conversion. They build a bridge between what the client needs and what your company can offer.
- Business growth. Sales representatives initialize referrals and help build customer loyalty.
- Client retention. Their connections with customers shouldn’t be under-evaluated. Remember that a 5% increase in retention rates may boost profits by 25%.
3. Analysis
Sales analysis concerns either KPIs and sales metrics. A key point here is to bring actionable insights that can be further used in the sales strategy. The following effectiveness indicators are usually used by most sales managers:
- Total revenue
- Revenue growth rate
- Revenue distribution by sources
- Revenue distribution by representatives
- Average conversion rate
- Sales-to-date
- Average purchase value.
Sales management process
Even though all team members contribute to commercial goals, it’s the manager’s responsibility to get the job done. Their tasks include:
1. Setting goals
To manage the process, you need to have a sales roadmap. With it, it’s possible to track the reps’ ongoing performance and timely determine whether comprehensive assistance is needed to achieve the goals.
2. Planning and managing sales activities
This area of responsibility concerns developing and testing sales activities. Trying out new technologies and approaches is the only way your team can succeed in nurturing customers better than competitors do.
3. Motivating the team
If you build team members’ competencies, you’ll boost employee retention and increase employee lifetime. Don’t become too experimental, however. Use good old methods of employee retention — the ones that have been tested by generations of managers:
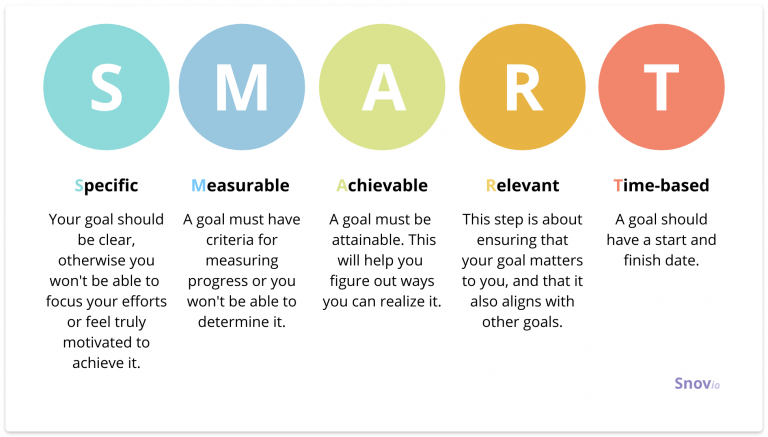
- Set SMART goals. A never-ending pursuit of unattainable results is exhausting and leads to emotional and professional burnout.
- Appreciate personal contribution. Gen Z are not the ones who will wait for changes — they want to lead them. If you value talent, be ready to give them enough space for initiative and decision-making.
- Build trust. Let each team member see the big picture and go over plans with your people. Share growth-hacking insights, corporate strategic goals, and how the company’s doing overall. If there are some issues — communicate these.
- Encourage high-performance culture. Cultivate a results-based work environment approach rather than just a work-to-do-work approach.
4. Evaluating and reporting
For every decision you make or insight you speak, put numbers in front. Use essential software, create sales dashboards, and deliver comprehensive sales reports. Make data integrated and visualize where relevant.
Using automation in your sales reporting will prevent:
- Revenue discrepancy
- Poor data access
- Decision-makers being overloaded with irrelevant and outdated information.
Effective sales management tactics
The best tactic is the one that brings you results. Whichever you adopt, make sure it doesn’t sound like “Increase sales by 500% the next month.” Just don’t. Numbers can’t be a tactic. A quarter of companies don’t even know if their salesforce achieves that quota.
Instead, focus on combining managerial best practices and come up with something that’ll boost your revenue:
1. Find the right people
Of course, staffing is a responsibility of the HR department. But for the manager, it’s crucial to translate vision and requirements to future employees to hire the right people.
The “right” doesn’t mean “the best”, though. Don’t look for Jack of all trades. Overloaded job descriptions are not effective. Define 2 or 3 key points that are relevant and go ahead hunting future sales reps.
2. Avoid “one-size-fits-all” decisions
Whatever you manage, people or processes, avoid oversimplification and too much extrapolation. What works in crisis may not work when the growth starts, and vice versa. Be flexible and an out-of-the-box thinker.
3. Hire specialists for different roles
If your business grows, you’ll have to divide responsibilities. One employee can’t combine several roles. As soon as you feel your workers can’t cope with the amount of work and tasks they get — hire more professionals.
4. Contribute to the growth of each sales representative
Best salespeople bring your company the most deals thanks to their experience, personal qualities, luck, or all three at a time. But if the team’s imbalance grows rapidly, you get a lot of deferred risks:
- Inner tension
- Loss of motivation
- Irreplaceable employees.
The manager’s task here is to understand why one sales rep performs much better than others and stabilize the situation. This is not about equalizing all, this is about finding points of growth for every team member.
Wrapping up
Sales team success largely determines your company’s overall performance because these guys bring in the revenue. Pay attention that the strategy and techniques used are relevant enough to achieve business objectives.















