On-target earnings (OTE)
OTE, short for ‘On-Target Earnings,’ signifies the total compensation an employee can potentially earn, including their base salary and commissions, assuming they meet specified sales targets or goals. If performance doesn’t match these expectations, the actual earnings may fall short of the projected OTE. It’s predominantly used in sales and other performance-based roles.

Let’s consider an on-target earnings example:
If your sales rep’s annual base salary is $60,000 and their on-target commission is $35,000, their OTE compensation will be $95,000, provided they hit all sales goals.
OTE = $60,000 + $35,000
OTE = $95,000
Importance of counting OTE compensation
There are several reasons companies use OTE as a sales compensation model:
- Team member motivation. Having a clear understanding of what goals a sales team should hit to get rewarded for their efforts, they feel more motivated to work harder and achieve better results.
- Higher productivity. Stimulated to get a decent bonus for their work, sales reps put more effort into fulfilling their tasks, which raises their productivity.
- Company’s growth. Feeling more encouraged to do a quality job, team members contribute to the business’s performance growth in general.
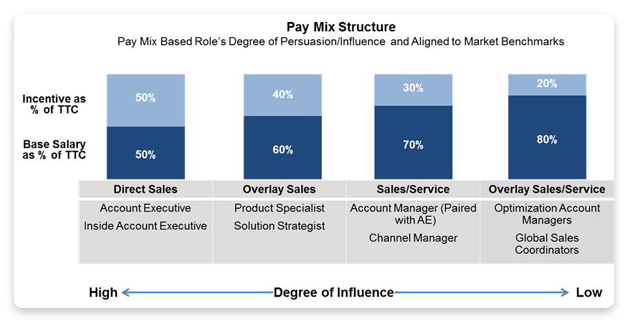
What is pay mix and how it relates to on-track earnings
To calculate OTE compensation, you should first determine a pay mix, i.e., a ratio of a base salary to variable pay (commissions). Say, if your pay mix is 75/25, it means your base salary makes 75% of the mix, while the commission is 25%.
What determines pay mix
There are several factors that influence the pay mix ratio:
- The sales position. Sales roles differ. A sales rep and a sales manager will have different job responsibilities and hence a different compensation ratio. Some positions require a more aggressive approach, which should be reflected by a higher pay mix.
- The length of the sales cycle. Longer sales cycles require more effort and motivation, so the pay mix should be higher in this case. By contrast, companies with a shorter sales cycle may have a lower mix because the sales team will close more deals in any given period.
- The product/service complexity. The more complex your offer is, the higher possibility you’ll wish to employ a sales rep who will be an expert in your industry, brand, and solution. Therefore, you’ll need a higher pay mix for motivating compensation.
- Company philosophy. One company may choose a high-degree of incentive in the mix to motivate sales reps, while another might use a conservative mix to mitigate risks. So, you need to understand what works better for your business and determine your pay mix correspondingly.
Let’s consider several pay mix ratio scenarios:
- 0:100 – Choosing this ratio, you push your sales reps to work independently and count only on commission. That’s not the best option since it will be rather stressful for them, which you’ll find hard to manage. If you still want to adopt it, you’d better arrange weekly payouts of commission to keep sales reps feeling rewarded.
- 50:50 – Such a ratio is good for the start. Your sales representatives will count on fixed pay and feel motivated enough to sell as they will get a considerable amount of commission.
- 90:10 – This ratio presupposes a small variable pay, hence little motivation for your sales reps to do their best closing sales.
When to consider a higher variable component of a pay mix
A higher variable component (percentage of commission) is recommended in cases when:
- The sales job is connected with pursuing new accounts.
- The selling is primarily direct.
- The price of the product or service is rather high.
- Internal career opportunities are overall limited.
When to consider a lower variable component of a pay mix
A lower percentage of commission is advised if:
- The sales position is not directly concerned with closing deals (e.g., a sales manager).
- The selling is primarily indirect.
- Your company is a startup.
- Internal career opportunities are relatively high.
How to calculate on-target earnings
Now that you understand how to determine a pay mix, you are ready to calculate OTE. We recommend to divide this process into four steps:
1. Establish your employee’s base salary
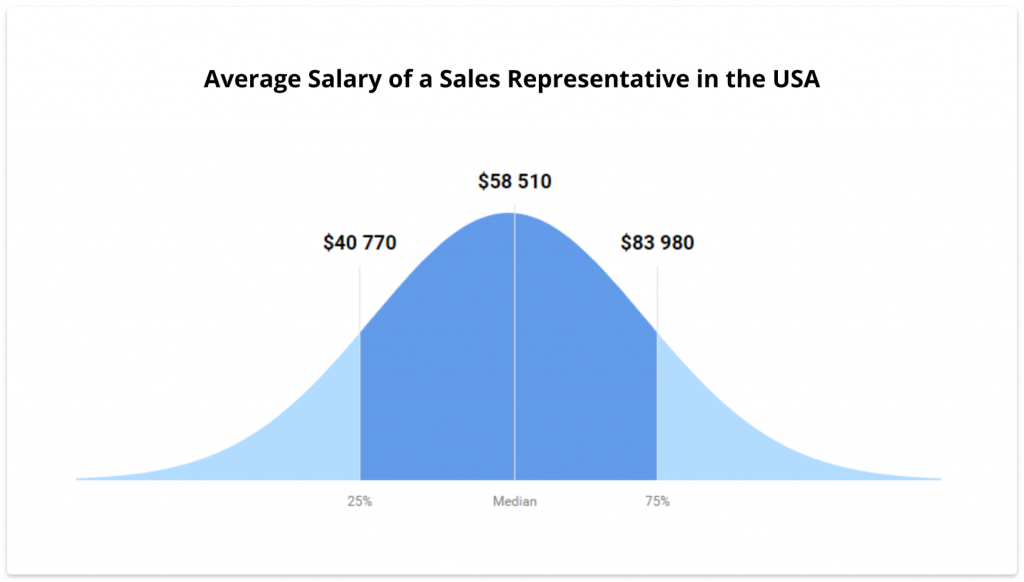
You won’t be able to count OTE compensation without establishing a base salary for your sales reps. This sum should compensate them enough for the quality of work they’ll do and match the standards of living so that they’ll have a decent income. A good piece of advice is to consider the average salary for the position that pertains to your country and industry.
2. Figure out the sales quota for your salespeople
Now it’s high time to determine the quota your sales reps will need to hit to earn a commission. It’s recommended to base sales OTE on one-fifth of the annual sales quota or 6 to 8 times the sales quota. You can also base it on a salespeople’s work experience.
3. Align commission with team goals
The commission part of OTE usually depends on the projected goals you want your sales team to meet. For example, it may be boosting revenue or increasing the amount of monthly closed deals by 8%, and so on.
Determine how difficult it will be to hit these goals and how long it may take. Align the commission with the complexity of achieving projected tasks.
4. Add the base salary together with the commission
Once you have determined the base salary and commission, add them together to get your OTE.
Wrapping up
Motivating your sales team is an effective way to boost your business’ revenue and ensure constant growth. OTE sales reps get stimulates them to work hard and achieve the company’s goals.
What you should always keep in mind is that OTE you offer to your salespeople must be simple enough to understand and agree to. Therefore, before coming up with a pay mix and an OTE strategy for all sales roles in a team, think well about the specifics of your sales process, the maturity of your product or service, and your company’s philosophy.
And when it comes to an effective sales strategy, Snov.io tools and guidelines are always in an on mode to help you build it from scratch.