Buyer behavior
Buyer behavior refers to the decision and acts people undertake to buy products or services for individual or group use. It’s synonymous with the term “consumer buying behavior,” which often applies to individual customers in contrast to businesses.
Buyer behavior is the driving force behind any marketing process. Understanding why and how people decide to purchase this or that product or why they are so loyal to one particular brand is the number one task for companies that strive for improving their business model and acquiring more customers.
Types of buyer behavior
Buyer behavior is always determined by how involved a client is in their decision to buy a product or service and how risky it is. The higher the product price, the higher the risk, the higher the customer’s involvement in purchase decisions. Based on these determinants, four types of consumer buyer behavior are distinguished:
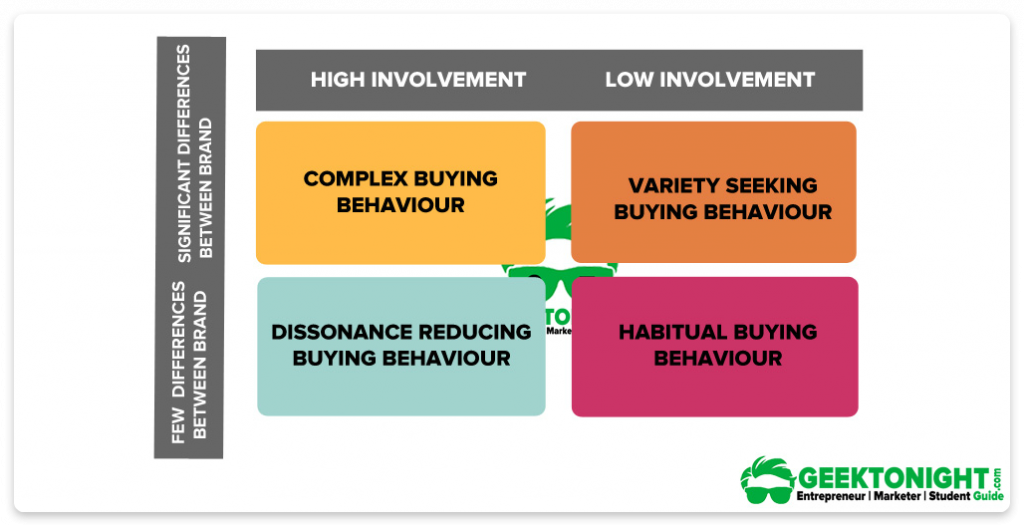
Complex buying behavior
This type is also called extensive. The customer is highly involved in the buying process and thorough research before the purchase due to the high degree of economic or psychological risk. Examples of this type of buying behavior include purchasing expensive goods or services such as a house, a car, an education course, etc.
Dissonance-reducing buying behavior
Like complex buying behavior, this type presupposes lots of involvement in the buying process due to the high price or infrequent purchase. People find it difficult to choose between brands and are afraid they might regret their choice afterward (hence the word ‘dissonance’).
As a rule, they buy goods without much research based on convenience or available budget. An example of dissonance-reducing buying behavior may be purchasing a waffle maker. In this case, a customer won’t think much about which model to use, chousing between a few brands available.
Habitual buying behavior
This type of consumer buying behavior is characterized by low involvement in a purchase decision. A client sees no significant difference among brands and buys habitual goods over a long period. An example of habitual buying behavior is purchasing everyday products.
Variety seeking behavior
In this case, a customer switches among brands for the sake of variety or curiosity, not dissatisfaction, demonstrating a low level of involvement. For example, they may buy soap without putting much thought into it. Next time, they will choose another brand to change the scent.
Buyer behavior patterns
Each consumer may have unique buying habits. Still, there are typical tendencies, which allows distinguishing the following buyer behavior patterns:
Place of purchase
If customers have access to several stores, they are not always loyal to one place. So even if all items are available in one outlet, they may divide their purchases among several shops.
Items purchased
There are two things to consider: the type of the product customers purchase and its quantity. As a rule, people buy necessity items in bulk. In contrast, luxury items are more likely to be purchased in small quantities and not frequently. The amount of goods people buy is influenced by such factors:
- Product durability
- Product availability
- Product price
- Buyer’s purchasing power
- Number of customers for whom the product is intended
The analysis of a buyer’s shopping cart may bring many valuable insights about buyer behavior.
Time and frequency of purchase
With the development of e-commerce, purchases have become only a few clicks away. Anyway, marketers should understand how often and at what time of the year or day people tend to buy more goods. The product purchase frequency may depend on the following factors:
- Product type
- Customer’s lifestyle
- Product necessity
- Customer’s traditions and customs
Method of purchase
People buy goods in different ways: some go to the store, while others prefer ordering items online. Some pay cash, while others use a credit card. Among customers who buy goods in online stores, some pay on delivery, while others are ready to pay right after they place an order. The way customers choose to purchase products tells a lot about their buyer persona.
Model of consumer buying behavior
The buyer behavior model is a structured step-by-step process. Under the influence of marketing stimuli (product, price, place, and promotion) and environmental factors (economic, technological, political, cultural), a customer understands the need to make a purchase.
The decision-making process they undergo afterward is affected by their characteristics, such as their beliefs, values, and motivation, resulting in the final decision to either buy or not to buy.
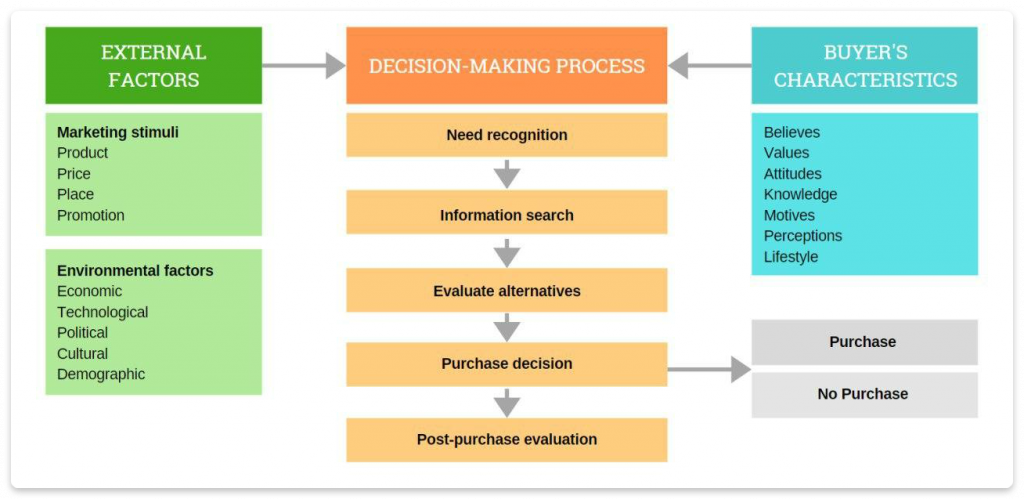
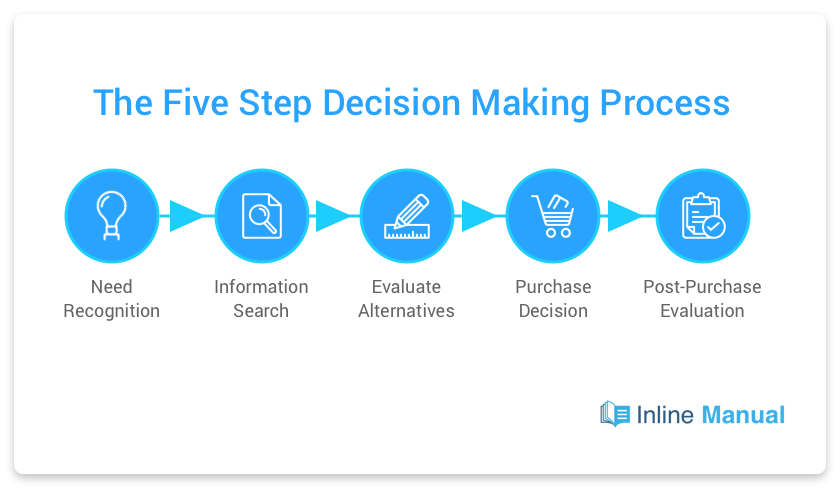
Most buyers go through several stages when making a purchase decision:
1. Need recognition
At the first stage, the buyer recognizes that there is a need for a product or service. For instance, they might realize that, since their company is growing, manual email outreach is no longer effective, so they need an email automation solution.
2. Information search
After understanding the need for a product or service, the buyer starts looking for information. They might obtain it from different sources (friends, commercials, mass media). For example, a prospect may start browsing email automation solutions, read reviews, etc.
3. Evaluation of alternatives
Once all the necessary information has been gathered, the buyer starts to evaluate a choice. They might compare key features and pricing, looking for advantages of one tool over all others.
4. Purchase decision
After evaluation, the buyer makes a purchase decision. For example, they start their free trial or purchase a paid plan.
5. Post-purchase evaluation
After purchasing the product or service, the buyer assesses whether it has met their expectations. At this stage, they might also leave an online review about the purchase or share their feedback with subscribers, colleagues, or friends.
There are cases, however, when some stages of the decision-making process are skipped. For example, the customer already knows a lot about a product and does not need to search for information. Another situation is when the buyer might see a product in the store and decide to buy it impulsively. Besides, there are situations when, after evaluating alternatives, the customer goes back to the information search step.
Buyer behavior analysis
To offer relevant products and services to the target audience, marketers should analyze what and how people buy. Companies adhere to several ways of monitoring consumer buying behavior:
Using computer software
Computer software provides companies with valuable information about the customers’ purchase experience. This allows analyzing what products or services are preferable among certain groups of buyers, how the customers’ location influences their purchase habits, etc.
Analyzing customers’ reviews
Another way of analyzing buyer behavior is to study the customer’s feedback. Online reviews can often reveal more than just people’s feelings about the purchase. They might also share some information about how they choose items or the way they prefer buying goods.
Conducting online surveys
Some companies also conduct online surveys, which gives them an opportunity to research the buyer behavior at any angle they need. Surveys allow requesting direct information about what people like to buy, what product qualities they value the most, what determines their purchase decision, and so on.
The analysis of buyer behavior tendencies will help companies find the right marketing strategies to attract potential customers and convert them.















