G2B
Relationships of a business with government agencies have a significant impact on the success of any company (and the economy, in general). This is primarily determined by how professionally the work with state bodies of various levels is organized and how well the processes are built by the government bodies.
Today, various levels of government have expanded their online presence due to the pandemic. Under the influence of external critical circumstances, they had no other choice than to update their internal processes for their subsequent automation to remain ahead of the curve.
Now we can see e-government taking shape in many countries, and providing electronic services (aka e-services) to businesses has become the new normal. However, there remains significant variation in the extent to which local governments deliver such assistance and information to companies.
Let’s take a look at what e-government is at its best and what an effective Government-to-Business (G2B) model implies, designed to support and develop businesses from the government’s side.
What is e-government?
Public authorities worldwide have been taking steps to involve technological communication devices in all governmental processes to ensure a faster and more transparent method of interaction with businesses, citizens, and other government agencies.
The e-governance implementation has got an incredible boost since the coronavirus pandemic outburst, allowing organizations to collaborate efficiently over distance.
According to United Nations’ definition, e-government comprises three integral parts:
- Government-to-Government (G2G) involves sharing data and conducting electronic communications between government agencies. This consists of intra- and inter-agency interactions at the national level and exchanges between the national, provincial, and local levels.
- Government-to-Business (G2B) refers to business-specific transactions (such as payments, selling and acquisition of goods and services, etc.) and the provision of business-focused services online.
- Government-to-Citizen (G2C) programs are meant to make it easier for citizens and consumers of public services to communicate with the government. This covers interactions, including the delivery of public services and participation in consultation and decision-making processes.
Some other sources, however, consider the above list incomplete and add one more component:
- Government-to-Employees (G2E) includes maintaining personal information and employee records. It also involves e-payroll (to view paychecks, pay stubs, pay bills, and keep records for tax information) and e-learning (to keep employees informed on the important materials they need to know through the use of visuals, animation, or videos via a computer-based learning tool).

Now it’s time we dive deeper into the Government-to-Business relationships and find out the points of contact at which businesses need government services. But first, let’s get down to definitions and check out the G2B meaning in more detail.
What is G2B?
Government-to-business (G2B) is a relationship between businesses and government, where government agencies of various levels provide services or information to a business entity via government portals or with the help of other IT solutions.
Such assistance from the government bodies’ side aims to facilitate swift and smooth business operations, as well as a fair and transparent environment to do business.
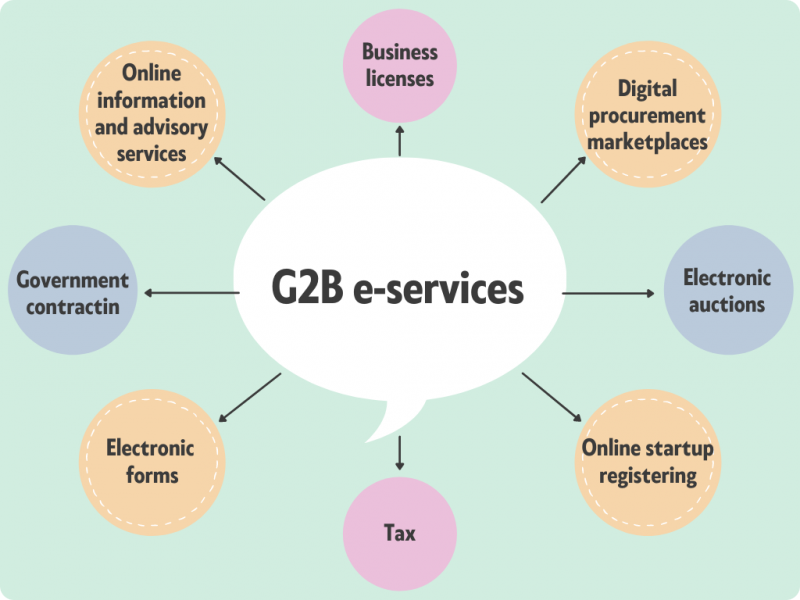
The range of the G2B services is broad. Below, you can see just a few of them:
- Online information and advisory services
- Government contracting
- Digital procurement marketplaces
- Business licenses, permits, and regulation updates
- Electronic auctions
- Tax, social insurance payments, and reporting
- Electronic forms
- Online application submission functionalities
- Virtual business dispute resolution
- Online startup registering
- Data centers, SaaS, PaaS, or IaaS for e-government use.
In the G2B model, the initiative comes from a government agency, and businesses are the target audience. In fact, businesses play the role of customers in the e-commerce model, and government agencies are, figuratively speaking, the customer support service.
In the globalized world, governments who succeeded in digitalizing their services and creating the most comfortable conditions for businesses and more fair market value will receive more foreign direct investment.
A difference between G2B and B2G: not to get confused
Unlike the G2B model, in B2G (Business-to-Government) relationships, the initiative comes from business. The official definition says that B2G is “the sale and marketing of goods and services to federal, state, or local agencies,” and B2G sales and marketing is oftentimes referred to as public sector marketing.
Most contracts between government agencies and companies are signed in response to an agency’s request for proposal (RFP). Businesses, in their turn, bid for contracts by submitting RFP responses. The bidding process can take place online in real-time and be highly competitive.
Considering the wide range of federal, state, and local purchasing requirements, an entire internet sector has developed to help match businesses to government agencies. For instance, a few well-known websites offer access to information on current U.S. government contracts: periscopeholdings.com, bidsync.com, thebidlab.com, and findrfp.com.
Wrapping up
The G2B model of interaction between government and business has been developing rapidly in recent years, ensuring a wide use of digital technologies across the economies and bringing benefits to everyone, from multinationals to small and medium-sized businesses.
And let’s consider that the state authorities borrowed this model from e-commerce, so its development and implementation can be viewed as a generous “return of debt” to the business community.















